See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/285684125
Retrobulbar Neuritis as the Initial Sign of Interferon-Alpha-Associated
Multiple Sclerosis in a Chronic Hepatitis B Patient: Case Report
Article in Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Medical Sciences · January 2011 DOI: 10.5336/medsci.2009-13361 CITATION 1 READS 32 4 authors, including:
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Hydroimplantation in pseudoexfolationView project Kemal Örnek
Ahi Evran Üniversitesi 108PUBLICATIONS 643CITATIONS SEE PROFILE Zafer Onaran Kirikkale University 57PUBLICATIONS 200CITATIONS SEE PROFILE
Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci 2011;31(3)
716
nterferon-alpha (IFN-α) is a natural glycoprotein produced by immu-ne cells in response to viral infections, and it is widely used to treat
chronic viral hepatitis.1Multiple sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune
dis-order characterized by demyelination in the central nervous system (CNS). Diagnosis of the disease is made according to the revised McDonald diag-nostic criteria for MS based on clinical, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
and laboratory findings.2Although the cause of demyelination remains
un-known, occasionally a theraupetic agent may promote an autoimmune pro-cess that attacks myelin. IFN-α associated MS has been reported in two
chronic leukemia patients (CML) and one chronic hepatitis C patient.3,4
Op-tic neuritis is one of the presenting features of MS in about 20% of
pati-Retrobulbar Neuritis as the Initial Sign of
Interferon-Alpha-Associated
Multiple Sclerosis in a
Chronic Hepatitis B Patient: Case Report
AABBSS TTRRAACCTT Interferon-alpha (IFN-α) is a therapeutic agent which plays an important role in the management of viral and malignant disorders. However, it has several side effects on eye and visual pathway. A 43-year-old man was admitted with sudden loss of vision. He had been on IFN-α treat-ment for chronic hepatitis B which was stopped 9 months earlier. The diagnosis of retrobulbar optic neuritis was made. Six months later, he admitted to us with decreased vision in the same eye. Mag-netic resonance imaging of the brain revealed white matter lesions. Further neurological investi-gations confirmed the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Multiple sclerosis should be considered in differential diagnosis of hepatitis B patients with a history of IFN-α treatment who present with vi-sual symptoms.
KKeeyy WWoorrddss:: Hepatitis B, chronic; interferon-alpha; multiple sclerosis; optic neuritis
Ö
ÖZZEETT İnterferon- alfa (IFN-α), viral ve malign hastalıkların tedavisinde önemli rol oynayan bir ajandır. Ancak göz ve görme yollarını etkileyen yan etkileri de bulunmaktadır. Kırk üç yaşında erkek hasta, tek taraflı görme kaybı şikayetiyle başvurdu. Hikayesinde kronik hepatit B tedavisi için uygulanan ve dokuz ay öncesinde kesilmiş IFN-α tedavisi mevcut idi. Hastaya retrobulber optik nörit tanısı kondu. Altı ay sonra aynı gözde görme kaybı ile tekrar başvuran hastanın beyin man-yetik rezonans görüntülemesinde beyaz madde lezyonları tespit edildi. İleri nörolojik değerlendir-mede multipl skleroz tanısı doğrulandı. IFN- α tedavisi alan hepatit B hastalarında ortaya çıkan görme şikayetlerinde multipl skleroz da ayırıcı tanıda düşünülmelidir.
AAnnaahh ttaarr KKee llii mmee lleerr:: Hepatit B, kronik; interferon-alfa; multipl skleroz; optik nörit
TTuurrkkiiyyee KKlliinniikklleerrii JJ MMeedd SSccii 22001111;;3311((33))::771166--99
Kemal ÖRNEK, MD,a Zafer ONARAN, MD,a Pelin YILMAZBAŞ, MD,a Sefa GÜLİTER, MDb Departments of aOphthalmology, bInternal Medicine,
Kırıkkale University Faculty of Medicine, Kırıkkale
Ge liş Ta ri hi/Re ce i ved: 07.05.2009 Ka bul Ta ri hi/Ac cep ted: 28.10.2009 Ya zış ma Ad re si/Cor res pon den ce: Zafer ONARAN, MD
Kırıkkale University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Ophthalmology, Kırıkkale,
TÜRKİYE/TURKEY drzaferonaran@yahoo.com
doi:10.5336/medsci.2009-13361 Cop yright © 2011 by Tür ki ye Kli nik le ri
Ophthalmology Örnek et al
ents.5He re we pre sent the first re port of a ret ro
bul bar op tic ne u ri tis in a chro nic he pa ti tis B pa ti -ent, pos sibly as so ci a ted with IFN-α-in du ced MS.
CA SE RE PORT
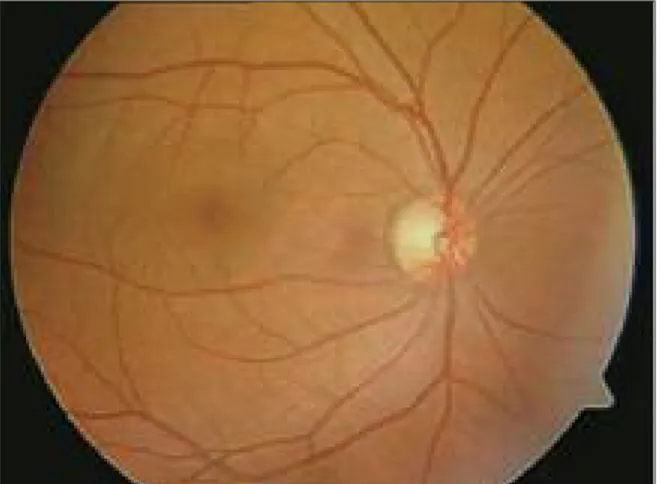
A 43-ye ar-old man ad mit ted to our cli nic with a sud den loss of vi si on in the right eye. He had be en on IFN-a tre at ment for chro nic he pa ti tis B which was in ter rup ted 9 months ear li er du e to syste mic si de ef fects. He had be en ad mi nis te red 9 mil li on units sub cu ta ne o us IFN-α thre e day a we ek for one ye ar. He had no his tory of ocu lar or any ot her sys-te mic di se a se. Best cor rec sys-ted vi su al acu ity in the right eye was co un ting fin gers from one me ter and it was 10/10 in the left eye. The re was no af fe rent pu pil lary de fect. Fun dus exa mi na ti on re ve a led bi-la te ral nor mal op tic discs (Fi gu re 1). Both pat tern and flash vi su al evo ked po ten ti al (VEP) re cor dings we re per for med. Pat tern VEP wa ve form in the right eye was dis tor ted and flash VEP was de la yed with lo wer amp li tu de with res pect to the left eye (Fi gu re 2). The re we re no pat ho lo gi cal fin dings in ne u ro lo gi cal and se ro lo gi cal tests. MRI of the bra -in and or bits was nor mal. Se ven days la ter, his vi-su al acu ity was me a vi-su red as 5/10. Ho we ver, co lor vi si on tes ted with Is hi ha ra pla tes was sig ni fi cantly re du ced. One month af ter, his vi su al acu ity was fo -und to be 8/10 and co lor vi si on 13/24 wit ho ut any tre at ment. Six months la ter, the pa ti ent was ad mit-ted to hos pi tal suf fe ring from dec re a sed vi si on (1/10) in the sa me eye. Fun dus exa mi na ti on was nor mal but bra in MRI de mons tra ted se ve ral whi te
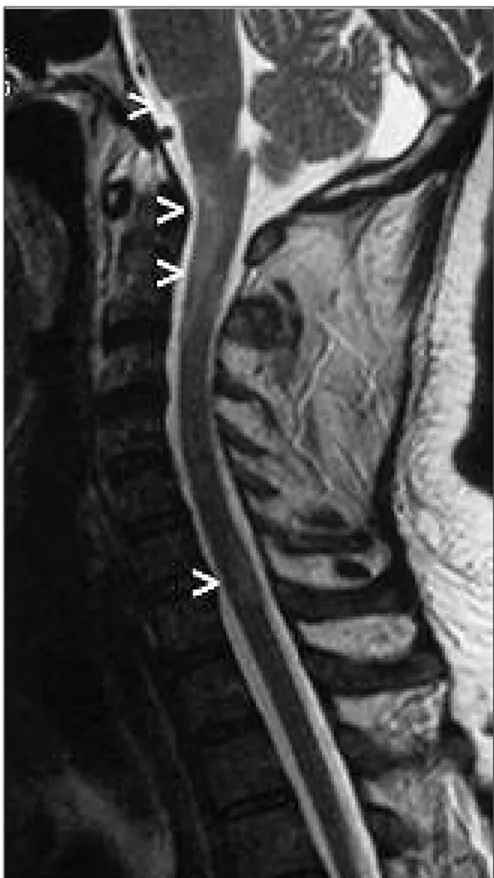
mat ter le si ons (Fi gu re 3). The re we re al so pat ho lo -gic sig nal en han ce ments which we re hype rin ten se in T2-we igh ted MRI of the spi nal cord (Fi gu re 4). Ne u ro lo gi cal exa mi na ti on re ve a led a po si ti ve Rom berg test and ata xi a. Lum bar punc tu re was per for med and exa mi na ti on of ce reb ros pi nal flu id sho wed oli goc lo nal bands and ele va ted IgG in dex (1.45). The se cli ni cal, la bo ra tory and ra di o lo gi cal fin dings met the re vi sed McDo nald cri te ri a and MS di ag no sis was ma de. Highdo se (1g/day) in tra ve -no us methy lpred ni so lo ne was gi ven for thre e days. As the pa ti ent had vi ral he pa ti tis as well oral ste ro -id ta pe ring was not per for med du e to risk of pro-lon ged ex po su re. Sig ni fi cant im pro ve ment was ac hi e ved in the vi su al acu ity (6/10) fol lo wing tre -at ment. The pa ti ent was tre a ted with in tra ve no us methy lpred ni so lo ne by ne u ro lo gists for two ti mes in the fol lo wing ye ar be ca u se of acu te exa cer ba ti -on of MS.
DIS CUS SI ON
Vi su al dis tur ban ces in chro nic he pa ti tis pa ti ents rece i ving INFα the rapy ha ve be en re la ted to va ri o -us pat ho lo gi es inc lu ding mul tip le scle ro sis-li ke di se a se, isc he mic op tic ne u ro pathy and re ti no
-FIGURE 1: Fundus of right eye showing a normal optic disc
FIGURE 2: Visual evoked potentials (pattern and flash) obtained from both eyes and were impaired in the right side.
Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci 2011;31(3)
718
pathy.3,4,6,7IFN is a le u kocy te-de ri ved cyto ki ne that
is a part of the chro nic he pa ti tis vi rus in fec ti on the -rapy. IFN has mul tip le ef fects on the im mu ne sys-tem and is known to trig ger the de ve lop ment of au to an ti bo di es, as well as the on set or exa cer ba ti on
of au to im mu ne di se a ses.8MS is an or gan-spe ci fic
au to im mu ne di se a se tar ge ting CNS mye lin. IFN-α in du ced MS has be en shown in CML and chro nic he pa ti tis C pa ti ents which we re ma ni fes ted du ring the the rapy or as long as 2 months af ter the ces sa -ti on of IFN-α. Our ca se dif fers from the ot hers in se ve ral ways. Our pa ti ent had chro nic he pa ti tis B who ini ti ally de ve lo ped ret ro bul bar op tic ne u ri tis and even tu ally prog res sed to CNS and spi nal cord dem ye li na ti on long af ter ter mi na ti on of IFNa the -rapy. Prog no sis of IFN-as so ci a ted MS has not be en well de fi ned sin ce it has be en pro po sed that ces sa ti on of the IFNα tre at ment co uld le ad to re mis si -on of the di se a se or may re sult in a ful mi nant
co ur se.9Gal li et al. re por ted the de ve lop ment of
ret ro bul bar op tic ne u ri tis in a pa ti ent with acu te he pa ti tis B in fec ti on, and they at temp ted to exp la -in the un derl y-ing pat ho ge ne sis with im mu ne
com-p le xes-me di a ted ne u ro to xi city hycom-pot he sis.10
In tra ve no us ste ro ids are of ten pres cri bed in ret ro bul bar op tic ne u ri tis to im pro ve vi su al out co -me or to dec re a se the long-term risk of mul tip le scle ro sis. Ho we ver, at the ti me of di ag no sis of op -tic ne u ri tis we he si ta ted to tre at our pa ti ent with ste ro ids du e to pre sen ce of a chro nic vi ral he pa ti tis. To ugh when MS was con fir med, he was tre a ted with ste ro ids un der the clo se ob ser va ti on of the in-ter nal me di ci ne spe ci a lists.
IFN has be en used cli ni cally to tre at nu me ro us vi ral and ma lig nant di se a ses. The re is a the ra pe -u tic di lem ma in terms of the -use of IFN-α in the ma na ge ment of MS as it co uld be both the ca u se of the di se a se and a the ra pe u tic op ti on. Mo re o ver, IFN the rapy may be as so ci a ted with ocu lar comp -li ca ti ons. Our ca se de mons tra tes an in di rect oph-thal mic si de ef fect of IFN-α sin ce it ca u sed MS. We be li e ve that MS sho uld be con si de red in the dif fe ren ti al di ag no sis of vi su al symptoms in chro nic he -pa ti tis B -pa ti ents with a his tory of IFN-α tre at ment.
FIGURE 3: Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain shows multiple periven-tricular and juxtacortical white matter lesions consistent with demyelination.
FIGURE 4: Pathologic signal enhancement in T2W spinal MRI at the level of brain stem, C1-3 and C6-7, indicating a demyelinating disease.
Turkiye Klinikleri J Med Sci 2011;31(3) 719
Ophthalmology Örnek et al
1. Gü ner İ, Öz men D, Ba yin dir O. [Cyto ki nes]. Tur ki ye Kli nik le ri J Med Sci 1997;17(2): 65-74.
2. Pol man CH, Re in gold SC, Edan G, Fi lip pi M, Har tung HP, Kap pos L, et al. Di ag nos tic cri te -ri a for mul tip le scle ro sis: 2005 re vi si ons to the “Mc Do nald Cri te ri a ”. Ann Ne u rol 2005;58(6): 840-6.
3. Mat su o T, Ta ka ba ta ke R. Mul tip le scle ro sisli -ke di se a se se con dary to alp ha in ter fe ron. Ocul Im mu nol Inf lamm 2002;10(4):299-304. 4. Ka ta o ka I, Shi na ga wa K, Shi ro Y, Oka mo to S,
Wa ta na be R, Mo ri T, et al. Mul tip le scle ro sis as so ci a ted with in ter fe ron-alp ha the rapy for
chro nic mye lo ge no us le u ka e mi a. Am J He ma-tol 2002;70(2):149-53.
5. Gil bert ME, Ser gott RC. New di rec ti ons in op -tic ne u ri tis and mul tip le scle ro sis. Curr Ne u rol Ne u ros ci Rep 2007;7(3):259-64.
6. Var di zer Y, Lin hart Y, Lo e wens te in A, Gar zo -zi H, Ma za wi N, Kes ler A. In ter fe ron-alp ha-as so ci a ted bi la te ral si mul ta ne o us isc he mic op tic ne u ro pathy. J Ne u ro oph thal mol 2003;23(4):256-9.
7. d'Al te roc he L, Maj zo ub S, Le cu yer AI, Delp la -ce MP, Bacq Y. Oph thal mo lo gic si de ef fects du ring alp hain ter fe ron the rapy for vi ral he pa -ti -tis. J He pa tol 2006;44(1):56-61.
8. Pre zi a ti D, La Ro sa L, Co vi ni G, Mar cel li R, Res cal li S, Per sa ni L, et al. Au to im mu nity and thyro id func ti on in pa ti ents with chro nic ac ti ve he pa ti tis tre a ted with re com bi nant in ter fe ron alp ha-2a. Eur J En doc ri nol 1995;132(5):587-93. 9. Höft ber ger R, Gar zuly F, Di e nes HP, Gru bits J, Ro hon yi B, Fisc her G, et al. Ful mi nant cen-tral ner vo us system dem ye li na ti on as so ci a ted with in ter fe ron-alp ha the rapy and he pa ti tis C vi rus in fec ti on. Mult Scler 2007;13(9):1100-6. 10. Gal li M, Mo rel li R, Ca sel la to A, Per na MC. Ret ro bul bar op tic ne u ri tis in a pa ti ent with acu -te type B he pa ti tis. J Ne u rol Sci 1986;72(2-3):195-200.