Selçuk J. Appl. Math. Selçuk Journal of Special Issue. pp. 19-26, 2012 Applied Mathematics
Selcuk Stat with Statistical Calculations and Performance Evaluation Ahmet Pekgör, A¸sır Genç
Selcuk University, Faculty of Science, Department of Statistics, 42031, Campus, Konya, Turkiye
e-mail: p ekgor@ selcuk.edu.tr, agenc@ selcuk.edu.tr
Presented in 3 National Communication Days of Konya Eregli Kemal Akman Vocational School, 28-29 April 2011.
Abstract. Mining, analysing and presenting data by statistical packages pro-vide their users the capability of modelling and foresight. Nowadays, by the virtue of technological improvement, users are empowered by various statistical packages against even most complicated statistical problems. But in current circumstances, to benefit completely from these packages, one must face various challenges. Two important criteria to choose one among competing packages may probably be the prices and the languages in which the packages are writ-ten. In this study, a free Turkish statistical package Selçuk STAT encoded with Delphi is compared with some other common statistical packages SPSS v17 and Minitab v15 in terms of their performance and speed.
Key words: Delphi, Selcuk STAT, Monte Carlo simulation. 2000 Mathematics Subject Classification: 68N19.
1. Introduction
Statistical methods are helpful for various fields ranging from natural and quan-titative sciences to social sciences like psychology, education and business. As-tronomers estimate the future positions of distant objects in space by statistical methods. Insurance companies calculate risk and premium payments on the basis of statistical records. By the principles of sampling theory, quality control experts make some inferential statements on the reliability of goods produced, etc. Although, the natures and some aspects of the events under investiga-tion and their interpretainvestiga-tions are thoroughly different from each other, these aforementioned areas use the same methodology. In other words, statistical procedures are applicable to most of the issues of scientific inquiry [2].
languages. It should be noted that a statistical program which provides the most convenience to its users in the immediate evaluation of output is highly appreciated [2]. Therefore, statistical packages provide some additional visual outputs or companions to software users as well as the results of complicated calculations in decison making processes.
New technology on computers with new visual computing technologies, new programming languages like Visual Basic, Visual C, Visual J++ and Delphi have begun to take the place the old in the field of computer programming languages. These visual programming languages should be grateful to application areas like data management, visualization and of course to the necessity to create some new faces to gain speed in calculations. Moreover, to be able to transfer data between various computer programs, some area facilities are developed. A “dialogue system” between human and computer, which is called the language of communication by visual programming should have definitely enlarged the area of practice [2].
Selçuk STAT software is an application created with the codes of Delphi pro-gramming language [1]. In particular the optical extraction is a Turkish dialogue and it requires minimal user intervention for the orders and the commands to be clear. Besides, it does not require any multi-featured computer. It is free and provides easy access to its leading features. In addition, Selçuk STAT software is easy to develop, and compatible with other programs that provide their users some additional facilities [2].
2. Selcuk Stat Program
Selcuk STAT ’s overall structure is a kind of database. Its interface consists of 4 main parts including calculations and preparing reports.
2.1. Database
Data entry by a package program also depends on the program’s database. The data base is a must-have item of the program. Here data sorting, storing, querying, deleting and handling of any such transactions are carried out on a worksheet. To perform an analysis of a data set as a priority, an interface to this data set must be kept. The program also uses one of the places which the users of the program think that thereby most of the data may be useful and with the idea that data will support other programs. The formation and organization of data in Selçuk STAT are realized by the menus at the top of the screen such as File (Dosya), Edit (Düzen) and View (Görünüm). Selçuk STAT also enables one in processing data by the data entry screen as shown in Figure 2.1.
Figure 2.1Data Entry Screen View
2.2. Interfaces
An analysis can be made easier and faster, largely depending on the design of analysis interface. Selçuk STAT in general and special designs can be used for each analysis. Statistical calculations used in overall interface design consist of the following steps:
a) Series of calculated data (column) names
b) The user selects the data to be used in the calculation keys c) To assign a region of the selected data
d) According to the analysis, special calculations, in order to attain, if nec-essary, and the analysis of the interface to exit the help file will give information about the special keys for achieving
Another way of going to “c” from “a” can also be realized by mouse, and keyboard keys. In designing interfaces, Selçuk STAT follows either the first or the second way[2]. For the second type of interface, a data entry screen; one does not need to specify column names. Data entry screen with a special key in data analysis, can be realized here and reselection with the help of a private key is possible. Figure 2.2 gives an example on a linear regression problem. The first type of interface design; user interface; and the second type of representing the data by sample matrix are shown in Figure 2.2.
Figure 2.2 Some of the designs of the Selçuk STAT interface
2.3 Calculations
Calculations are necessary for analysing the results. The user selects a type of analysis here not only by way of menus and interfaces. After selecting an analysis, the mathematical and statistical computations are performed . As the results of calculations, user will see the reporting section that contains tables and/or graphics. As can be emphasized here, except one user’s own computa-tions, all computations are realized in the background. Selçuk STAT is helpful in carrying out more than 500 calculations. Some main titles in this respect are matrix operations, tables of statistical distributions [3], random numbers, classification of data and descriptive statistics, cross-tables, correlation and co-variance, parametric and nonparametric hypothesis testing, linear and nonlinear regression analysis [4], analysis of variance, clustering analysis, operations re-search and simplex methods, QQ, PP and 3-D visual graphics.
2.4 Reporting
It is important for the users to interpret the results by easy and accurate re-ports. Reporting in a seperate package to user interface programs, post-analysis, graphics are offered by a data entry screen. External reporting, and graphical interfaces are designed in Selçuk STAT. At the reporting part, the data entry screen has a different appearence.
Figure 2.3Reporting interface view
The graphical user interface has the following appearance.
Figure 2.4 Graphical interface views
3. Application
Selçuk STAT was compared with SPSS v17 and Minitab v15. The comparisons are based on the performances on the following issues: Random number
genera-The figures were obtained in a computer with the following features: Windows XP SP3, Intel Core Duo2 2GHz processor, 2GB RAM and NVIDIA GeForce 9600 GT Graphics card.
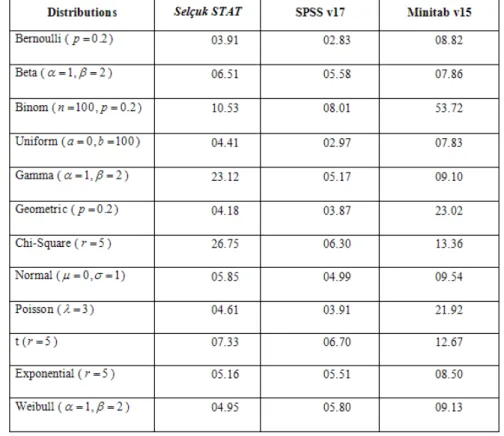
Table 3.1Performances of statistical packages on random number generation
The results are summarized on Table 3.1 as shown above. SPSS showed the best performance whereas Minitab the worst.
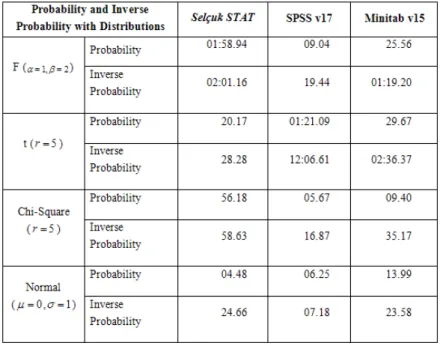
F, student-t and chi-square distributions are three frequently-used probability distributions in both hypothesis testing and confidence interval estimation pro-cedures since they are closely related to normal distribution or “normality as-sumption”. Therefore probability and inverse probability calculations for these distributions are extremely important. Table 3.2 summarizes the performances of three packages for probability and inverse probability calculations.
Table 3.2Performances of statistical packages on calculating probabilities and inverse probabilities
Except for student t-distribution, SPSS has the leading figures in this respect. Again Minitab showed poor performance than the others.
Table 3.4Performances of packages on graphic modules
From the table 3.4 given above one can state that there is not a significant difference between these three packages.
4. Results and Discussion
In terms of speed, of the operations on random number generation, probability and inverse probability calculations, hypothesis testing procedures and graphic modules, there is not a significant difference between the packages (p0.05) However, it should be emphasized that Selçuk STAT package as a free package program is on the same level with the other two in terms of speed and per-formance. This is a result in agree with the view that Selçuk STAT is really a contribution -at least based on the arguments of this paper- to statistical package programming.
5. Acknowledgements
This study is a part of Master Thesis. Thesis titled “Statistical Calculations and Data Analysis with Delphi: Selçuk STAT”, Ahmet PEKGÖR, submitted by Sel-cuk University, Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Department of Statistics, Konya, Turkey, 2004.
References
1. Cantu, M., "Delphi7: Uygulama Geli¸stirme Kılavuzu", YA ˘GCI, D.A., Alfa Basım Yayım Da˘gıtım, ˙Istanbul, 2003.
2. Pekgör A., "Statistical Calculations and Data Analysis with Delphi: Selçuk STAT", Master Thesis, Selcuk University, Graduate School of Natural and Applied Sciences, Department of Statistics, Konya, Turkey, 2004.
3. Press, W.H., Teukolsky, S.A., Vetterling W.T., Flannery, B.P., "Numerical Recipes in C", Cambridge University Press, USA, 2002.
4. Seber, G.A.F., Wild, C.J., "Nonlinear Regression", John Willey & Sons, Inc., Canada, 1989.