The communication skills and school achievement among the students: A
review of the students at vocational high schools
Article · August 2015 CITATIONS 0 READS 87 2 authors, including:
Some of the authors of this publication are also working on these related projects:
Benlik sunum aracı olarak Instagram kullanımı View project Veysel Çakmak
Aksaray Üniversitesi 13PUBLICATIONS 10CITATIONS
SEE PROFILE
All content following this page was uploaded by Veysel Çakmak on 07 March 2018. The user has requested enhancement of the downloaded file.
Copyright The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology
551
The Communication Skills And School Achievement Among The Students: A Review Of
The Students At Vocational High Schools
Veysel Çakmak
Aksaray University, Aksaray Social Sciences Vocational School, Aksaray, Turkey veyselcakmakk@gmail.com
Musa Küçük
Aksaray University, Aksaray Social Sciences Vocational School, Aksaray, Turkey musakucukmyo@hotmail.com
ABSTRACT
Human being is in communication with his/her environment. This interaction is generally in the form of interpersonal communication. The person performs it according to his/her communication skills. The communication skills are the ability of making more than one senses when he/she encounters the events. In the research, the Communication Skills Inventory developed by Ersanlı and Balcı (1998) was used. This scale analyzes the level of communication skills from the points of its behavioral, cognitive and emotional dimensions. In the study, the communication skills of the students, their school achievement and other variants are analyzed. The study is conducted on the students of Aksaray University, Aksaray Vocational High School of Social Sciences. The study was limited with the expressions in the data collecting instruments.
Keywords: communication, communication skills, school achievement, INTRODUCTION
Communication is a system which forms the base of the society. It is an instrument makes the method work effectively, a technique affecting the personal behaviors, an obligatory science from the point of social relations or an art necessary social adaptation. Thus, the answer to the question of “Why do people communicate” may be given as knowledge, persuasion, management, sharing, sharing the differences, amusement, changing, problem solving and cooperation (Küçükaslan, 2014; 6). Communication is a human activity which is known by everybody, yet only a few people can completely define it. The samples of communication can be listed as talking face to face, television, information dissemination, hairstyle, literary critics, walking style of the individual etc. (Fiske, 2014;71)
Communication is divided into two groups such as source module and target module. The source module is the module which sends the message. It may be a talking person, a meowing cat or a computer playing chess. The target module is the module which the message is sent. The talking module is the source while the listening module is the target module when two people talk (Cüceloğlu, 2001;68).
Two basic elementary ideas emerge when the approaches are considered in explaining the term communication. The first of them reveal the direction of the communication process. This is an approach characterized with the model of sender-message-channel-receiver. In those models, it is stated that an attitude, an emotion and an idea is transferred to the other side. Other approaches are mutually and common perceiving and sharing (Mutlu, 2012;149).
Communication skills are the basic factors in eliminating or decreasing the conflicts in establishing an effective and correct communication and abilities related to speaking, writing, reading, listening and thinking (Toy, 2007; 14). Thus, the individuals having effective communication skills in their daily and business life will have increased success rate.
One of the basic factors affecting the School Achievement of the student is the attitudes of parents. Parents desire to do their best for their children and contribute to the development of their children. Since the rights of mothers and fathers are different from each other, however, their attitudes to their children also vary. The basic stones of the personality of the child begin during the pre-school age and continue until university age. The attitudes of the parents set an example to the developing child, the child imitates whatever he/she sees and starts to shape his/her personality through internalizing those attitudes. For that reason, the parents have to behave according to the behavior model they expected from their children (Gümüş, Kurt, Ermurat, & Feyetörbay, 2011).
Other factors affecting the School Achievement of the students are vulnerability of focusing and motivation. Such deficiencies, if prioritized, may be listed as follows; being unable to find a job after university, environmental and noise pollution, health problems, bad friends, inter-parental conflicts, economic insufficiency, the problems of transportation, terror and violence, and the problems of housing (Katipoğlu, 2012).
Numerous studies were conducted in both Turkey and the world on the various variants of communication skills. Some of those studies are as follows.
Copyright The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology
552
When the relationship between the communication skills and sub-dimensions of resolving interpersonal problems is analyzed, there is a positive relationship between communication skills and total score of skills for resolving interpersonal problems (Koç, Terzi, & Gül, 2015). According to the research conducted on various sectors, however, no significant difference was observed in terms of the age variant of communication skills. Moreover, no significant difference was obtained in terms of educational levels of the employees (Örücü & Kıvrak, 2013).
METHODS
The Communication Skill Inventory (Scale) was used in the research. This scale was developed in 1998 by Ersanlı and Balcı through conducting the validity and reliability checking. There are three basic sub-dimensions in the scale such as behavioral, cognitive and emotional dimensions. Moreover, the School Achievement was tackled as another variant. The data of the scale was obtained from 168 students studying in the first year of Aksaray University Aksaray Vocational High School of Social Sciences in the Spring term of 2014-2015 Academic Year. In the study, Communication Skills Inventory developed by Ersanlı and Balcı (1998) was used. This scale analyses the levels of communication skills from the behavioral, cognitive and emotional dimensions. The scale consists of 45 narrations. The items in the scale were scored as “always 5”, “generally 4”, sometimes 3”, “rarely 2” and “never 1”. Maximum score to be obtained is 224 while the minimum score is 45. The high levels of scores in the entire scale mean that the individual got high scores while the lower total scores indicate that the individual received lower marks. Moreover, there are 15 items for each sub-dimension. Each sub-scale may be separately analyzed as well as evaluating the general communication of the individual through considering the total scores of a scale. The maximum score for sub-dimension is 75 while the minimum score is 15. As seen in the general communication ability, the higher levels of ability mean high scores and low levels mean the lower scores. (Ersanlı & Balcı, 1998). SPSS 15.0 program was used in order to analyze the data obtained within the scope of the research. The descriptive statistics were used in the analysis of the data, Pearson correlation analysis were used to determine the relationships between variants, the ANOVA test was used instead of parametric test assumptions in order to determine the
differences between the variants and Kruskal-Wallis test was applied when the assumptions don’t become true.
Moreover, Cronbach’s Alpha test was applied in order to measure the consistency of the answers to the questions in the questionnaire and internal consistency coefficient of Cronbach’s Alpha was found as 0,844. Namely, 84,4% of the responses given by the participants of the questionnaire is reliable and consistent.
Copyright The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology
553
FINDINGSThe related characteristics of the students and families are given in Table 1.
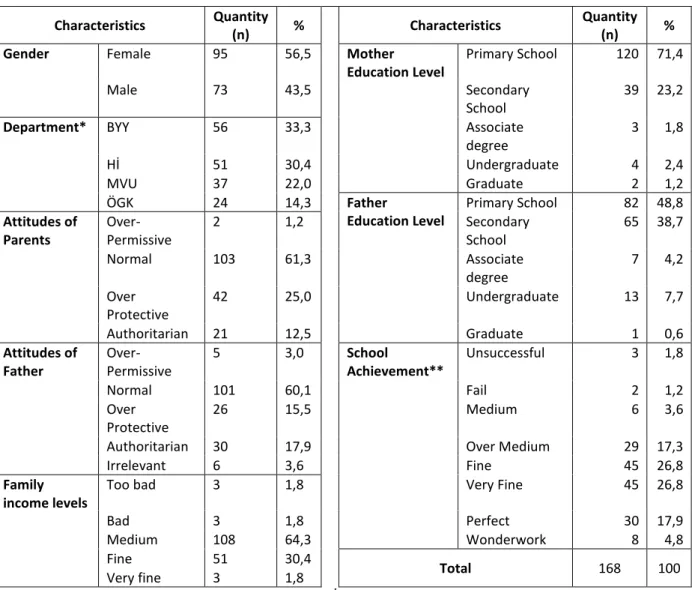
Table 1: The Frequencies of the Students and Families related to their Characteristics
Characteristics Quantity
(n) % Characteristics
Quantity
(n) %
Gender Female 95 56,5 Mother
Education Level
Primary School 120 71,4
Male 73 43,5 Secondary
School
39 23,2
Department* BYY 56 33,3 Associate
degree 3 1,8 Hİ 51 30,4 Undergraduate 4 2,4 MVU 37 22,0 Graduate 2 1,2 ÖGK 24 14,3 Father Education Level Primary School 82 48,8 Attitudes of Parents Over-Permissive 2 1,2 Secondary School 65 38,7 Normal 103 61,3 Associate degree 7 4,2 Over Protective 42 25,0 Undergraduate 13 7,7 Authoritarian 21 12,5 Graduate 1 0,6 Attitudes of Father Over-Permissive 5 3,0 School Achievement** Unsuccessful 3 1,8 Normal 101 60,1 Fail 2 1,2 Over Protective 26 15,5 Medium 6 3,6
Authoritarian 30 17,9 Over Medium 29 17,3
Irrelevant 6 3,6 Fine 45 26,8
Family income levels
Too bad 3 1,8 Very Fine 45 26,8
Bad 3 1,8 Perfect 30 17,9
Medium 108 64,3 Wonderwork 8 4,8
Fine 51 30,4
Total 168 100
Very fine 3 1,8
*BYY:Office Management and Executive Assistance ,Hİ: Public Relations and Publicity ,MVU: Accounting and Tax Practices, ÖGK: Private Security Protection
** Wonderwork (3,51 – 4), Perfect (3,01 - 3,50), Very Well (2,51 – 3), Well (2,01 - 2,50), Over Average ( 1,51 – 2), medium (1,01 -1,50), Poor(0,51-1), Unsuccessful (0 - 0,50)
Within the scope of the study, 168 students participated the research. Among them: 56,5% (95) of them are Female while 43,5% (73) of them are Male students. Among the students who participated the research, 33,3% (56) are the students of Office Management and Executive Assistance, 30,4%(51) are Public Relations and Publicity, 22% (37) of them are Accounting and Tax Practices and 14,3% (24) of them are the students of Private Security Protection department.
When the school achievements of the students are analyzed, 1,8% (3) of them was unsuccessful, 1,2% (2) of them was poor, 3,6% (6) of them was medium, 17,3% (29) of them was over medium, 26,8% (45) of them was fine, 26,8% (45) of them was very fine, 17,9% (30) of them was perfect and 4,8% (8) of them had the level of Wonderwork.
In this study, the communication skills were analyzed in three sub-groups. They are cognitive (mental) communication skill, emotional communication skill and behavioral communication skill. Within the scope of the research, total scores related to the communication skills were used. Moreover, total scores of communication
Copyright The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology
554
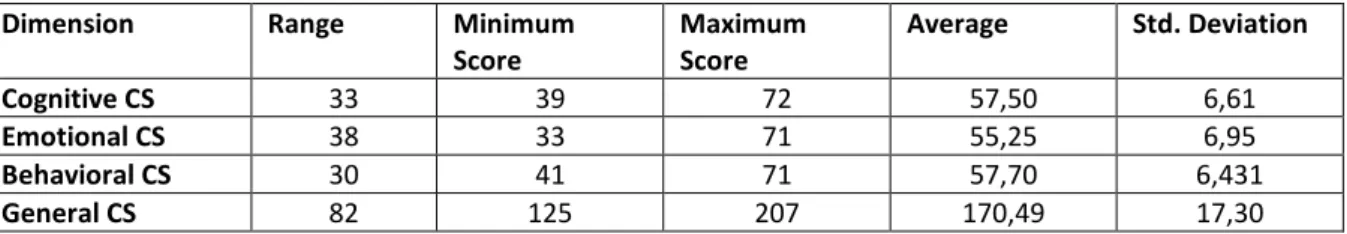
Table 2: The Descriptive Statistics Related to Communication Skills and Sub-dimensionsDimension Range Minimum
Score Maximum Score Average Std. Deviation Cognitive CS 33 39 72 57,50 6,61 Emotional CS 38 33 71 55,25 6,95 Behavioral CS 30 41 71 57,70 6,431 General CS 82 125 207 170,49 17,30
The maximum score which general communication skill can obtain is 225 and minimum score is 45 while the maximum score in general communication skills according to the descriptive statistics given in Table 2 was 207 and the minimum of that was 125 and the arithmetic average was 170,49. Accordingly, it can be said that the communication levels among the students are high. When the sub-groups are considered, the emotional communication skill levels are seen to be lower than others and the scores of cognitive and behavioral communication are very close to each other.
In order to decide whether to use the parametric test or a non-parametric test in testing the significance of the difference between the school achievement and communication skill levels, we should consider the assumptions of normality and homogeneity of the variances.
H0: groups are normally distributed.
H1: groups aren’t normally distributed.
Table 2: The values related to the normality test of the groups Shapiro-Wilk GROUPS p Cognitive CS 0,203 Emotional CS 0,018 Behavioral CS 0,168 General CS 0,129
As seen in the values given in Table 2, the result of Shapiro-Wilk normality tests applied to the variants was found p>0,05 for cognitive CS, emotional CS and General CS. Namely, those variants are convenient for normal distribution. However, behavioral CS doesn’t have the normal distribution due to its value of p<0,05. In this occasion, ANOVA test will be used to measure whether the difference between cognitive CS, emotional CS and General CS and the school achievement is significant; and Kruskal-Wallis test will be used in order to measure whether the difference between behavioral CS and the school achievement is significant.
First of all, ANOVA test can be applied in case the variances for the variants of cognitive CS, emotional Cs and General CS which provide the normality assumption are homogenous. The results of Levene Test performed to
test the homogeneity of the variances are given in Table 3.
H0: The variances between the groups are equal.
H1: At least one group has different variance than the others.
Table 3: The Test for Homogeneity of the Variances
Levene Test S.D.1 S.D.2 p value
General CS 1,005 7 160 0,430
Cognitive CS ,450 7 160 0,869
Emotional CS 1,384 7 160 0,215
The hypothesis that the result of homogeneity test conducted for General CS, cognitive CS and Emotional CS is
p>0,05 H0 was accepted. Namely, the variances are homogenous and the assumptions of the normality and
homogeneity of the variances were proved in order to perform ANOVA test.
H0: There is no significant difference between cognitive CS, emotional Cs and general CS from the point of
school achievement.
H1: There is a significant difference between cognitive CS, emotional Cs and general CS from the point of
Copyright The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology
555
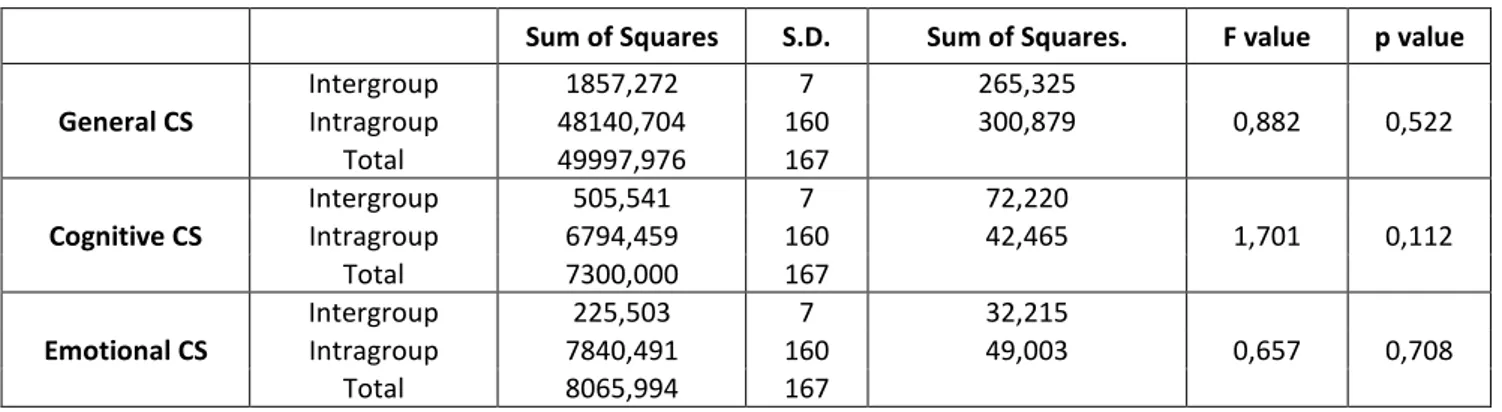
Table 4: The Values of the Effect of General Communication Skill, Cognitive Communication Skill andEmotional Communication Skill on the School Achievement
Sum of Squares S.D. Sum of Squares. F value p value
General CS Intergroup 1857,272 7 265,325 0,882 0,522 Intragroup 48140,704 160 300,879 Total 49997,976 167 Cognitive CS Intergroup 505,541 7 72,220 1,701 0,112 Intragroup 6794,459 160 42,465 Total 7300,000 167 Emotional CS Intergroup 225,503 7 32,215 0,657 0,708 Intragroup 7840,491 160 49,003 Total 8065,994 167
According to the result of ANOVA Test, H0 hypothesis is accepted since general communication skill is
p=0,522>0,05, cognitive communication skill is p=0,112>0,05 and emotional communication level is p=0,708>0,05. Namely, general CS, cognitive CS and emotional CS have no effect on the school achievement. In Table 5, the results of Kruskal Wallis test which is used in the analysis of the differences between behavioral communication skill and school achievement which doresen’t prove rhe hypothesis.
H0: There is no statistically significant difference between school achievements, behavioral communication skills.
H1: There is a statistically significant difference between school achievements, behavioral communication skills.
Tablo 5: The values of the effect of behavioral communication skills on School achievement
School Achievement n Mean Rank
p
valueBehavioral CS Unsuccessful 3 43.67 0.564 Fail 2 109.50 Medium 6 76.25 Over Medium 29 82.98 Fine 45 85.11 Very Fine 45 89.60 Perfect 30 75.87 Wonderwork 8 105.50
According to the results of Kruskal-Wallis test, it was found that p=0,564 > 0,05. In this case, the hypothesis of
H0 is accepted.There is no statistically significant difference between the school achievements and the averages
of behavioral communication skill. Namely, behavioral communication skill has no effect on school achievement. Finally, the relationship between the school achievements of the students, their communication skills and sub-groups was analyzed through. The values of correlation coefficients are given in Table 6.
Copyright The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology
556
Table 6: The relationship between school achievement, general communication skills and sub-groupsSchool Achievement
General CS Cognitive CS Behavioral
CS Emotional CS School Achievement 1 School Achievement 0,134 1 School Achievement 0,192* 0,883** 1 School Achievement 0,056 0,,875** 0,706** 1 School Achievement 0,095 0,845** 0,592** 0,592** 1
*Correlation is significant at the level of 0.05 (2-ways). ** Correlation is significant at the level of 0.01 (2-ways).
Cognitive CS, behavioral CS and Emotional CS have positive and highly relationships with each other. For example, the student with high cognitive communication skills also has both high behavioral communication and emotional communication skills; thus, he has high general communication skills. If the cognitive communication skill is low, the other communication skills will also be low.
We can state that the levels of communication skills have a very slight effect on the school achievement. It means that the student with high levels of communication skills may have lower school achievements.
CONCLUSIONS
In the study, the communication skills and their school achievements were aimed to research. The study was conducted on 95 female and 73 Male students with a total of 168 who study at Aksaray University. The attitudes of the parents of the students were normal in the rate of 60%. It was concluded that mothers are more Over-protective than fathers.
Communication skill and its sub-group consisting cognitive, emotional and behavioral communication skills are in the interaction with each other however they have no effect on the school achievement.
A student with high school achievements may not have high communication skills. Hence, the student with low school achievement doesn’t mean that he has low communication skill. Namely, it is not true to decide about school achievement considering the school achievement.
References
Cüceloğlu, D. (2001). Yenien İnsan İnsana (26 b.). İstanbul: Remzi Kitabevi.
Ersanlı, K., & Balcı, S. (1998). İletişim Becerileri Envanterinin Geliştirilmesi: Geçerlik ve Güvenirlik Çalışması. Türk Psikolojik Danışma ve Rehberlik Dergisi, 7-12.
Fiske, J. (2014). İletişim Çalışmalarına Giriş (3 b.). (S. İrvan, Çev.) Ankara: Pharmakon Yayinevi.
Gümüş, İ., Kurt, M., Ermurat, D. G., & Feyetörbay, E. (2011). Anne-Baba Tutumu ve Okul Başarısına Etkisi. Ekev Akademi Dergisi(47), 423-443.
Karasar, N. (2012). Bilimsel Araştırma Yöntemi (23 b.). Ankara: Nobel Yayınevi.
Katipoğlu, B. (2012). Öğrencilerde Dikkat ve Motivasyon Zafiyetine Neden olan Bazı Faktörler. Balıkesir Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi, 15(27), 225-235.
Kaya, A. (2011). Etkili ve Güzel Konuşma Sanatı (3 b.). Konya: Eğitim Kitabevi.
Koç, B., Terzi, Y., & Gül, A. (2015). Üniversite Öğrencilerinin İletişim Becerileri ile Kişilerarası Problem Çözme Becerileri Arasındaki İlişki. Uluslararası Türkçe Edebiyat Kültür Eğitim Dergisi(4/1), 369-390. Küçükaslan, N. (2014). Etkili İletişim Teknikleri. Bursa: Ekin Basın Yayın Dağıtım.
Mutlu, E. (2012). İletişim Sözlüğü (6 b.). Ankara: Sofos Kıta Basım Dağıtım Yayıncılık.
Örücü, E., & Kıvrak, O. (2013). Telekomünikasyon Sektöründe Çalışan Personelin İletişim Becerileri Düzeylerinin İncelenmesi. Yönetim ve Ekonomi, 20(1), 14-29.
Toy, S. (2007). Mühendislik ve Hukuk Fakülteleri Öğrencilerinin İletişim Becerileri Açısından Karşılaştırılması ve İletişim Becerileriyle Bazı Değişkenler Arasındaki İlişkiler. Ankara Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü.
View publication stats View publication stats