T.C.
ISTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF GRADUATE STUDIES
THE FACTORS AFFECTING THE ADOPTION OF ONLINE BANKING SERVICES BY CIVIL SERVANTS IN CAMEROON
Lith Enestine TEMBON AMBIT
Department of Business Administration Business Administration Program
iii T.C.
ISTANBUL AYDIN UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF GRADUATE STUDIES
THE FACTORS AFFECTING THE ADOPTION OF ONLINE BANKING SERVICES BY CIVIL SERVANTS IN CAMEROON
MBA THESIS
Lith Enestine TEMBON AMBIT (Y1812.130126)
Department of Business Administration Business Administration Program
Thesis Advisor:
Prof. DR. ERGINBAY UGURLU
iv
DECLARATION
I hereby declare with respect that the study “the factors affecting the adoption of online banking services by civil servants in Cameroon”, was submitted as a Master thesis and written without any assistance in violation of scientific ethics and traditions in all the processes from the Project phase to the conclusion of the thesis.
v FOREWORD
My profound gratitude goes to God for His mercy and unconditional protection. I also appreciate my supervisor Prof. Dr. Erginbay UGURLU for the advice and academic support during the program. Furthermore, special thanks to my family and friends especially my parents who provided me with unlimited support for the success of this project.
I dedicate this work to the Almighty God.
vi TABLE OF CONTENTS Page DECLARATION ... iv FOREWORD ... v TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vi ABSTRACT ... viii ÖZET ... ix 1.INTRODUCTION ... 1 1.1. Study Overview ... 1 1.2. Problem Identified ... 2 1.3Study Questions ... 3 1.4. Other Objectives... 3 1.5. Study Hypotheses ... 4
1.6. Significance of the Study ... 4
1.7. Study Scope ... 5
1.8. Operational Definition of Terms ... 5
2. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 6
2.1.Banking Service ... 6
2.2. Online Banking ... 6
2.3. Acceptance of Online Banking ... 9
2.4. Adoption of Internet Banking ... 11
2.5. Trust, Apparent Risk and Electronic Banking ... 12
2.6. Pros and Cons of Internet Banking to Emerging Economy ... 13
2.7. Organization Reputation ... 14
vii
2.9. Internet Banking Services and Client Satisfaction ... 16
3.REVIEW OF LITERATURE ... 19
3.1. Gap in the Literature ... 26
4.MEHTODOLOGY ... 27 4.1.Research Design ... 27 4.2. Population ... 27 4.3. Sampling ... 27 4.4. Validity ... 28 4.5. Reliability ... 29 4.6. Research Tool... 29
4.7. Model Specification and Framework ... 29
4.8. Conceptual Framework ... 30
4.9. Description of Proxy ... 31
4.10.A-priori Expectation ... 32
5.DISCUSSION OF ANALYSIS ... 33
5.1.Demographic and Descriptive Analyses ... 33
5.2. Frequency Result ... 38 5.3. Crosstabs Analysis ... 47 5.4. Descriptive Analysis ... 48 5.5. Reliability Result ... 49 5.6. Factor Analysis ... 49 5.7. Correlation Result ... 50 5.8. Regression Result ... 51 5.9. Study Findings ... 52
6.CONCLUSION & KEY RECOMMENDATIONS ... 55
REFERENCES ... 58
viii
THE FACTORS AFFECTING THE ADOPTION OF ONLINE BANKING SERVICES BY CIVIL SERVANTS IN CAMEROON
ABSTRACT
The factors affecting the adoption of online banking services by civil servants in Cameroon was examined in this research. For this research statistical analysis was used. The information for the analysis was obtained from raw data. The raw data were gotten through questionnaire which was distributed mostly among the civil servant in some part of Cameroon. The analyses used in this survey are frequency analysis, factor analysis, correlation analysis and regression analysis. Different concepts were discussed in the section two of this survey ranging from the online involvement with banking structure and strategy, civil servant attitude and internet adoption, reputation of organization, quality and customer satisfaction. The findings revealed that awareness factor a positive and significant effect on online banking. It was concluded that internet banking is difficult to understand and its time consuming among many of the users and internet fraud discourages the use of internet banking in Cameroon. Additionally, the dissemination of information through the internet is not mostly secure and efficient and using internet banking is difficult for the older customers so, they mostly go against online banking in Cameroon.
ix
KAMERUNDA SİVİL HİZMETLERLE ONLINE BANKACILIK HİZMETLERİNİN KABUL EDİLMESİNİ ETKEN FAKTÖRLER
ÖZET
Bu çalışmada Kamerun'da çevrimiçi bankacılık hizmetlerinde çalışan memurlar tarafından benimsenmesini etkileyen faktörler incelenmiştir. Bu amaçla istatistiksel analizler kullanıldı. Analizde kullanılan veriler, Kamerun'da çalışan memurlar arasında dağıtılan anket yoluyla elde edildi. Bu ankette kullanılan analizler frekans analizi, tanımlayıcı istatistikler, faktör analizi, korelasyon analizi ve regresyon analizidir. Bu araştırmanın ikinci bölümünde bankacılık yapısı ve stratejisine çevrimiçi katılım, memur tutumu ve internetin benimsenmesi, organizasyonun itibarı, kalite ve müşteri memnuniyeti gibi farklı kavramlar tartışıldı. Bulgular, farkındalık faktörünün çevrimiçi bankacılık üzerinde olumlu ve anlamlı bir etkiye sahiptir. İnternet bankacılığının anlaşılmasının zor olduğu ve birçok kullanıcı için zaman alıcı olduğu ve internet dolandırıcılığının Kamerun'da internet bankacılığının kullanılmasını engellediği sonucuna varıldı. Ek olarak, bilgilerin internet aracılığıyla yayılması çoğunlukla güvenli ve verimli olmadığı ve internet bankacılığını kullanın yaşlı müşteriler için zor olduğu ve bu nedenle Kamerun'da çoğunlukla çevrimiçi bankacılığa karşı oldukları saptandı.
Anahtar Kelimeler: Çevrimiçi Bankacılık, Müşteri Hizmetleri, Memnuniyet ve Kamerun
1
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1. Study Overview
The issues affecting the use of internet services of the banks by civil servants in Cameroon cannot be over-emphasized. Banks play a crucial role in the financial formulation of any nation and exhibit a substantial role in the growth and development via competent services (Al-Smadi, 2012). Banks offer linkage between borrowers and lenders, surplus and deficit units, resulting to form investment. Some years ago, banking services have been faced with different changes connected with financial liberalization and globalization. Due to the technological changes or modernization, banks develop different choices of services accessible to the existing and potential customers and increase their reliance on technology. Banking sector is one of the inclined sectors accepting technologies which are obliging in producing improved services to clients. Technological innovations improve the quality of service and safe transaction time (Safeena, Abdullah, & Date, 2010). Online banking uses web as a means of rending services such as funds transfer, paying bills, opening of account, buying financial instruments and the like (Haque et al. 2009 as cited by Samsunia, 2016).
The bank service delivery can be competent when the contextual processes are well-organized. An effective contextual process could be achieved when it is cohesive with electronic settings. The mechanisms such as hardware, data, app, web and customers are the crucial basics of the structure. The clients become fulfilled through service once it springs the greatest expediency and solace of service execution (Singhai & Padhmanabhan, 2008). The swift advance of web advancement and circulation of cell phones, online banking has attracted attention in offering financial services. Online banking offers monetary transactions services like fund transfer and pay bills through
2
cell phones device and smart phone. In looking for enhancements in client involvement, financial societies have instigated subscribing various online banking services. Online banking is a way of exploring possibility to use internet app in one of the several domains of commerce. The only way that banks could be allied to their clients at any location and time is via online applications (Singhai & Padhmanabhan, 2008). Luo, et al. (2010) online banking offers new cost saving prospects for banks, decreasing operation costs, diminishing error in transactions and reducing fraud, producing extra revenue via commissions and service fees, and increasing retention and loyalty among customers.
1.2. Problem Identified
Although online banking accompanies a swarm of risks and security dangers yet at the same time an ever-increasing number of banks are utilizing the advantages the online needs to convey banking services to clients/customers. Banks have applied online banking to offer customers a variation of services with more suitability for accessing information and making transactions (Safeena, Abdullah, & Date, 2010). Flavian et al. (2006) viewed that the customers and the banks appreciate the online banking system in such a way that its cost decreases and extends market and clients then again appreciates a more extensive scope of products and convenient banking because of the pervasive idea of the internet. In any case, non-presence of security is the premier obstruction factor in the progression of web banking reception among clients (Flavian et al. 2006). Additionally, different issues that impact the client’s intensions to receive web banking are the clients' returns, gender and maturity. Besides, Amin (2009) carried out an investigation and found out that issues influencing a consumer to admit or reject the practice of online banking are the deceptive usefulness, comfort of usage, and social norms were significant whiles alleged pleasure were unimportant to the adoption of online banking on consumers behave. The review conducted by other studies on the subject such as Kolodinsky et al. (2004); Pikkarainen et al. (2004); Yiu et al. (2007); Chan and Lu (2004); depicts that many studies were carried out in
3
developed countries. In contrast, few studies were carried out in developing countries such as Jabnoun and Al-Tamimi (2003); Al-Somali, et at. (2009).
1.3. Study Questions
Online banking services have been faced with different challenges in the financial system of different countries especially the developing and under-developed nations of the world. However, the following questions are aimed to provide answer to:
i. How does innovative factor affect online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon?
ii. Does security and trust factors affect online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon?
iii. How does customer service assurance impact on online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon?
iv. How does awareness factor affect online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon?
1.4. Other Objectives
The broad objective is to investigate the factors affecting the adoption of online banking services by civil servants in Cameroon. However, the specific objectives are stated as:
i. To examine the innovative factor on online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon.
ii. To investigate the impact of security and trust factors on online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon
4
iii. To determine the effect of customer service assurance on use online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon
iv. To survey the effect of awareness factor on online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon
1.5. Study Hypotheses
The hypotheses are stated in null form below:
Ho1: Innovative factor does not have an effect online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon
Ho2: There is no significant impact between security and trust factors on online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon?
Ho3: Customer service assurance does not have an impact on online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon
Ho4: Awareness factor does not have an effect on online banking services among civil servant in Cameroon
1.6. Significance of the Study
This study aimed to determine the issues affecting the use of online banking services by civil servants in Cameroon. It will provide an insight view about how civil servant views online banking in Cameroon. The finding of this study will be essential to the managers, civil servant, bank operators, investors, government and policy makers. It will expose the various linkages in the banking services in relation to customer convenience and satisfaction. It will also add to the factors that impede cost of the services and means of overcoming them.
It will assist the policy makers to gain proper understanding of the magnitude and asymmetry of bank service for effective policy making in the financial service. Lastly,
5
the new knowledge gained from the study would benefit students and other researchers working on the factor affecting the adoption of bank service in Cameroon.
1.7. Study Scope
The study shall mainly focus on Civil Servant in Cameroon. Cameroon is in Central Africa with area covered of about 475,650km2 (183,650sq.mi). it has about 24million population and has about 250 ethnic groups with 270 African languages and dialects. However, the commercial capital of Cameroon (Douala) will be major focused. Douala has about 1.3million people comprised of civil servant and non-civil servant. The civil servant will be majorly used as the target audience in this study.
1.8. Operational Definition of Terms
Innovative: this implies the perception as a submission of purposes that enhance new necessities, tacit needs or existing market desires
Customer Service Assurance: this refers as the procedure intended to maximize efficiency and offer solutions in which revolves around satisfying customer and maximizes the enterprise profitability.
Trust: this indicates the consistent and persistent of the services the customer received over time.
Online: this is the means of using internet channels as a means of interaction between business to customer and customer to business
6 2. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1.Banking Service
Banks are means of storing and lending organizations that offer different forms of
accounting services (Xue, Hitt & Chen, 2018). Service charges linked to transactional depository account is one of the largest charge’s components of a bank. Because of the moderately significant expense and huge client perceivability of the exercises, banks
are main adopters of technology for improving their tasks. Banks offer different
services to customers to perform financial transactions: ATMs, telephone-based
communication, and automated withdrawals systems. Online banking offers the ease
access of banking services anywhere, with token adoption expenses for their
customers who have online access, which does not require much skill from the
customers. Based on bank's point of view, online channel is appealing since it might
diminish service charges legitimately or may change over the variable expense of
employee’s service channels to the to a great extent fixed cost technology framework, in this way expanding economies of scale
2.2.Online Banking
Banks have utilized online networks to carry out banking activities with their clients.
Recently, financial institutions are using online means to get guidelines and
7
assumed by banks about the online shift generally in element, which is known as
internet banking. Online banking definition differs among scholars, according to
Daniel (1999), online banking implies a sort of administrations in which clients can
demand info and complete banking services via processor, TV or mobile
communication. Internet banking is the exchanging of services via internet networks
that includes electronic plantation and connectivity of services through electronic
means. This can consolidate store enchanting, advancing, the course of action of
budgetary device, electronic charge portion, and the game plan for various things and
organizations, for instance, electronic money. The electronic banking as yielded a
technique channel to motivate in achieving high ground and augmentation a bit of the
general business. Also, electronic administrations can spare the expense of assets,
which are required for customary financial administrations (Jayawardhena et al. 2000).
Aladwani, (2001) proposed that e-banking gives quicker, simpler and increasingly
solid administrations to clients. Be that as it may, clients are still sluggish to adopt
online financial services, because they are timid of the security situation and have
inadequate capacity to handle the electronic banking platform.
Electronic banking (e-banking) is a banking instruments, expected to the clients,
lawfully structured/designed, which allows installment of payments, exchanging
transaction, cash transaction record to another, etc. Electronic banking is utilized in
connection with PC and internet, regardless of the location of the participant.
8
include the use of electronic, internet and mobile technologies (Kim et al., 2011).
E-banking system signifies a range of systems ranging from automated teller machines
(ATMs), electronic banking, computer banking, cable banking, Online banking and,
most recently, smartphone banking (Parker & Parker, 2008). Such technologies are
rapidly widespread in the banking sector and are used to offer better services to
consumers seeking simplicity and technology-savvy and to minimize banks' operating
costs (Nasri, 2011). Internet and mobile banking have been the leading distribution
platforms used by banks to service their clients in line with customer demand and
higher returns and market conditions (Moutinho & Curry, 1994).
For all intents and purposes, the client of this administration does not need to own a
PC, an internet outlet is helpful for such service. Indistinguishable activities exist for
online banking: transmission of installment orders, transfer, perspective on the records'
circumstance and so forth. Banks began to hop over the essential phase of online
banking, straightforwardly to Internet Banking. The speedy binge of online banking all
through the universe is due to its affirmation as a financial savvy channel of banking
activities that makes it to appear differently in relation to other existing channels.
According to Solanki (2012), the decline in cost of trades; it has also accomplished
another bearing uncertainty and new sorts of threats that transmit online banking.
The regulators universally are concerned and with the goal for banks to stay
productive and savvy, they need different kinds of issues this type of banking involves
9
significant component is that, the idea exhibits a noteworthy effect on the source and
device for directing the uncertainty. In view of the growing idea, there exist no
significant solution to the measures or the uncertainty. Electronic banking could be
depicted as an "umbrella" term, which is utilized reciprocally once individuals allude
to at least one structure or segment of e-banking, for example, virtual banking, online
banking, digital banking, intuitive banking, telephone banking, and electronic banking.
2.3.Acceptance of Online Banking
Online banking leads to the use of the web of a bank from which clients view their
bank accounts, make banking transactions and receive general knowledge on banking
goods and services. It is a type of "internet portal" that helps consumers to connect
conveniently with a bank by providing them with the ability to access banking services
online and everywhere in the world (Casalo, Flavián, & Guinalíu, 2007).
Advancements in IT have significantly affected the development of more accessible
payment systems and more user-friendly online banking (Akinci, Aksoy & Atilgan,
2004). The exponential expansion of the Internet has also fundamentally altered the
distribution networks used by the financial services sector. Online banking as a service
delivery platform has gained traction due to low transaction costs and a broad range of
user base connectivity options (Shah & Siddiqui, 2006). The financial sector has
introduced e-banking as an e-commerce method with better banking infrastructure and
10
of bank customers by delivering services at any time and everywhere (George &
Kumar, 2013).
Technological advances play a crucial part in human and technical life. The
exponential growth of technology has absorbed hundreds of people into their lives.
Rapid developments in technology have brought significant improvements to the
global economic and business climate (Qureshi, Zafar, & Khan, 2008). Marketing
research and the online banking had showed many influences that predicted the
mindset of customers towards internet banking, such as demographics, confidence and
attitudes towards various banking technology and individual tolerance of new
technologies. It was discovered that the attitudes of consumers towards online banking
are affected by existing system and digital media background (Laforet & Li, 2005).
The introduction of online banking causes customers to address questions about the
security of codes, anonymity, data encryption, intrusion and safety of personal
information (Benamati & Serva, 2007). Electronic banking may require the consumer
engagement because it allows the user to manage and communicate frequently with
additional technologies such as computer and connective (Jane, Hogarth, & Hilgert,
2004). Customers who use online banking use it constantly and need to gain a certain
degree of familiarity with the product in order to continue using it (Servon &
Kaestner, 2008). With the technological context of usage, the level of use and the
period of product use have been developed to measure the use of product by the
11
perceived risk to measure the attitude or intention of the customer to use online
banking.
2.4.Adoption of Internet Banking
Internet advances in the financial industry have flown up activities and dealings for
customers. Internet banking is one of the ways that are fastest rising banking activities
nowadays (Safeena, Abdullah, & Date, 2010). The online has an ever-growing
standing in the banking service due to the rewards it conveys to both the sector and
their client. While Internet outflow is viewed costly and dicey, financial services are
one of the major investors in information system (Mashhour & Zaatreh, 2008).
Internet is inexpensive transfer network for banking services as it permits the entity to
reduce or increase their branch networks and downscale the number of service staff.
The navigability of the site is a significant part of Internet banking since it can wind up
chances of a financial entity (Ortega et al. 2007). Bankers choose to limit cost of
exchanges and efficient to be significant advantages and odds of government access,
odds of misrepresentation and absence of data security to be imperative dangers
associated with internet banking (Kaleem & Ahmad, 2008). Because of the usage of
technology growing, the banking industry efficiency rises day by day. Banking
industry is one of the inclined industries implementing technologies that are
supportive in rendering improved services to clients, this left Internet banking to
becomes the crucial part of advanced banking administrations. Service quality is
12
The adoption by customer is a known predicament designed for the implementation of
tactical form of financial institutes. A few investigations have researched why people
pick a bank. Some client factors incorporate comfort, services facilities, notoriety and
loan costs (Zineldin, 1996). As per Delvin (1995), clients have limited time carrying
an activity, for example, going to a bank and in this manner need a sophisticated level
of suitability and availability. The quality of service internet banks required to actuate
clients to change to internet means and continue utilizing them are apparent
usefulness, convenience, dependability, receptiveness, safety, and ceaseless
enhancement. An investigation conducted by Liao et al., (2002), revealed that the
assumptions of precision, speediness, ease of use, and customer inclusion are the
utmost significant effective characteristics in the apparent helpfulness of e-banking.
2.5.Trust, Apparent Risk and Electronic Banking
Currall and Judge (1995) suggested trust as a person’s sureness on another under states
of dependence and hazard. A person’s trust actions depend on the idea of the
occasions. In some area, for example, web banking, hazard fudging may ascend since
lessening hazard offsets cost reserve funds. Mayer et al. (1995) are of the view that
dependence is the tendency to acknowledge chance, whereas trust refers to the
supposition of hazard. In the study of (Lewicki & Binker, 1995), they opined that
confidence/trust creates after some time. Trusting an individual about an item/product
diverse relying upon when trust is evaluated. More so, in this way, on the off chance
13
trustor will take part in a hazard taking affiliation. Trust in bank dealer and its web
implies are imperative given that there is some hazard tangled in utilizing web
channels for exchange.
Some articles acknowledged a deficiency of trust as the crucial obstacles to client’s
usage of internet transaction (Luarn & Lin, 2005; Mukherjee & Nath, 2003; Flavian,
Guinaliu, & Torres 2006). In the study conducted by Tan and Teo (2000), opined that
hazard toward via the online among the influences of intents to assume online banking
services. Kassim et al. (2006) and Vatanasombut, Igbaria, Stylianou, & Rodgers
(2008) revealed that trust doesn’t only influence commitment to embrace internet
banking then aids online banking. More so, Casaló, Flavián, and Guinalíu (2007);
Lichtenstein et al. (2006) said that trust displayed a prominent part in embracing of
internet banking application. Additionally, Pavlou, (2003) said that trust is useful tool
in dropping the perceived uncertainty that client’s sense is extant in an internet setting.
2.6.Pros and Cons of Internet Banking to Emerging Economy
Recently, the expansion in technology has affected businesses in many conducts,
particularly in area of control, research and development, activities, and basic
leadership. It is in this way, the vogue that each business aims to gain accrue from
technology advancement. The introduction of technology has presented high running
cost and substantially improved the efficiency of business organizations. Masocha et
al, (2011) viewed that banks change their focus towards using automation and internet processes. The internet process distribution of banking service has become ideal for
14
banks to attaining clients’ hopes and create near client relationship (Ching, 2008).
However, online banking will overcome old form of banking in the forthcoming, since
many developing countries seem to diversify their focus on infrastructure with specific
reflection on e-commerce, electronic-business and electronic-learning (Kamel, 2005).
Electronic banking starts with straightforward dimensions, for instance, ongoing
admittance to information about cost, transaction records regulates and processing
credit requirement. Nonetheless, these administrations have transferred to online
installment, move of assets in cash management administrations for business
associations and people (Khan, Mahapatra, & Sreekrumah, 2009).
The improvement knowledge of internet and other overall online frameworks have as
such made new attachment open entryways for electronic business and development of
new plans of worldwide and national trading associations. This, therefore, provoked
the acumen that e-banking and online business are by and by an unavoidable piece of
cash related organizations (Harris & Spencer, 2002).
2.7.Organization Reputation
The selection models propounded were produced for contemplating innovation
appropriation in advanced nations, in any case, innovation appropriation in advance
nations may be not quite the same as the developing nations as the difficulties are
diverse in different settings (Molla & Licker, 2001). Tornatzky and Fleischer
postulated technology organization environment in 1990 illustrating three elements
15
technology setting, business setting and environmental setting. Technology setting
incorporates both inside and outside advancements relevant for firm. Business setting
incorporates assets (capital and human), business extension and size. Environmental
setting incorporates both the immediate and aberrant jobs of contenders, industry
affiliations, and the governments. Subsequently, Tan and Teo (2000) assumed firm
reputation as a variable for deciding reception of e-banking in Singapore. They
reported that bank reputation is significant in picking an online banking facility. The
assortment of administrations accessible and commonality with the banks are likewise
significant criteria.
2.8.Civil Servant Attitude and Internet Adoption
Civil servant behavior and desires to banking innovations are a vital factor in the
improvement of effective electronic banking execution ventures (Lymperopoulos &
Chaniotakis, 2004). If civil servant mainly reflects e-banking as a self-administration
and invaluable channel that decrease costs and if its determination won't impact their
reserve funds, by then they will receive it. Be that as it may, if they see e-banking as a
peril to their save finances possibilities and a way to deal with lose customers, by then
they will most likely restrict its gathering to keep the traditional form of banking
services. Civil Servant struggle to the adoption of technology is a general issue in the
banking sector mostly in the developing countries. The introduction of new
technologies will undeniably cause a worrying influence in organizations and to
16
dislodged by new ones (Davis et al. 1989). They further view that the effective usage
of any new technology is chiefly controlled by organization clients' frames of mind:
workers and administrators build a mentality and feeling about the new technology,
and that feeling could guide them to the reception or dismissal of the proposed
technology. Attitude can be an exceptionally incredible empowering agent or an
obstruction towards the appropriation of the new technology. Attitude is defined
according to Ajzen and Fishbein (1980) as a multifaceted puzzle of feelings, wishes
and worries that generate a means of eagerness to act within an individual.
2.9.Internet Banking Services and Client Satisfaction
Online banking service has been one of the banks' traditional methods of delivering
services to their customers. Online banking refers to the way banks use online
platforms to sell consumers financial goods and services (Al-Smadi, 2012). Electronic
banking is a modern form in financial transfers, which has caught many banks'
imagination as an alternative to conventional banking. It is a highly
information-intensive operation that relies heavily on the internet to obtain, structure and provide
all users with financial information (Alkailani, 2016). It provides various services to
customers including; bill payments, balance enquiry, forex, loan repayments, opening
account statements etc. Many banks have not used e-banking to optimize their full
capacity, which gives banks the incentive to transfer their customers to e-platforms.
The unavailability of information protection and internet thoughtfulness in banking
17
bank accounts. Other considerations found by writers to be a considerable difficulty
are the system's unreliability, which has proved to be unreliable due to technical
difficulties, connections & network problems, which are apparent from the numerous
interruptions faced by users due to connectivity issues (Hussain et al., 2017). Existing
research has described a few reasons that may contribute to low technology adoption
through different hypotheses of technology adoption which illustrates the perceived
ease of use, perceived usefulness as variables influencing e-banking acceptance.
Client satisfaction is portrayed as a get-together of the aftereffects of acknowledgment,
appraisal and mental reactions to the usage inclusion with a product/service (Saha &
Zhao, 2005). They further characterized consumer fulfillment as a scholarly and
loaded with feeling evaluation where some relationship standard is diverged from the
truly seen presentation. When the perceived outcome is less than projected, clients will
be displeased. In return, when perceived outcome is more than projected, a client will
be pleased. Boateng and Molla (2006) concur that functioning restraints identified
with client area, the need to keep up consumer loyalty and the abilities of the Bank's
primary programming are compelling components in spurring the choice to enter
internet banking processes and subsequently impacting the use understanding and, in
this manner, influencing the degree of fulfillment.
Raman et al. (2008) supposed that service as a subtle decent intrigue distinctively to
each customer and certain level of service ought to be attained to fulfill the client and
18
loyalty. A highly loyal clients consume additional goods or services, spring more
clients and are not likely to move to other bank outlet, contrasted with other clients
that have lesser commitment levels. However, Casaló et al. (2008) fight that more
elevated levels of internet ease of use may prompt more significant levels of buyer's
full of feeling pledge to the internet, positive and huge connection between fulfillment
in past communications and the shopper's promise to internet banking service.
Wangenheim and Bayòn, (2004) characterize client loyalty as a profoundly commitment to habitually rebuy a similar item or service.
19 3. REVIEW OF LITERATURE
The review comprised of three aspects, which include conceptual clarifications,
theoretical issues and past study review. The past study review relating to the factors
affecting the adoption of online banking services by civil servants in Cameroon is
presented below:
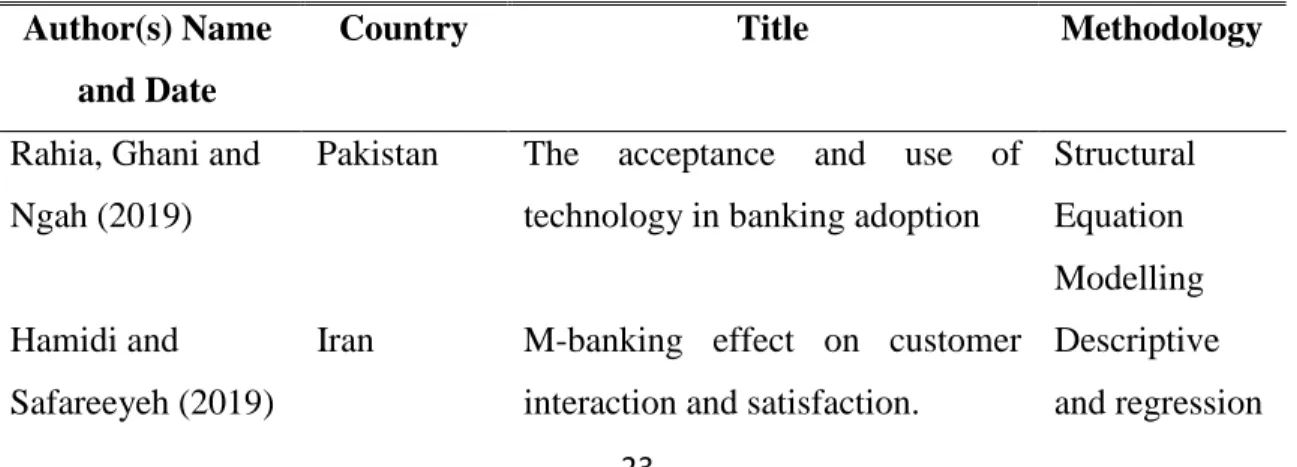
Vetribvel, Rajini and Krihnamoorthy (2020) wrote on the effect service quality of
online banking on consumer fulfillment in India. The regression results revealed a
positive correction between the quality of internet banking and consumer fulfillment.
Rahia, Ghani and Ngah (2019) wrote on the acceptance and use of technology in
banking adoption in Pakistan using 398 banks customers. Structural equation
modelling was conducted, and the results revealed that the most powerful factor that
influences the adoption of e-banking is assurance among all others. Hamidi and
Safareeyeh (2019) examined m-banking effect on customer interaction and satisfaction
in Iran. Questionnaire was used to collect data from the participants using descriptive
and regression analysis. The findings revealed that the variables used are statistically
positive to customers’ interaction and satisfaction excluding trust. Merhia, Hone, and Tarhini (2019) carried out a study on the intention to use mobile banking services
20
between Lebanese and British consumers. The data was gathered through
questionnaire to 901 applicants and employed SEM technique. The study found that
the adoption of mobile banking services was influenced by habit, perceived security,
perceived privacy and trust for both the Lebanese and English consumers.
Alalwan, Baabdullah, Rana, Tamilmanic, and Dwivedic (2018) investigated the
adoption of mobile internet in Saudi Arabia. Questionnaire was distributed to the
selected elements of the population using structural equation modelling. They found
that the adoption of mobile internet by Saudi customers is motivated with trust,
innovativeness, perceived usefulness and enjoyment which are statistically significant.
Jansen and Schaik (2018) wrote on testing online behavior in banking sector of
Netherlands. Partial least square path modelling was used in the study and the results
revealed that there exists high level of variance for precautionary online behavior.
Jehan and Ansari (2018) conducted a survey in Saudi Arabia on the adoption of
internet banking. The descriptive analysis revealed that trust is the most prominent
aspect for the internet banking acceptance. Alalwana, Dwivedi, and Rana (2017)
considered the influences inducing the acceptance of mobile banking by Jordanian
banks where 343 respondents were participated in the survey using structural equation
modelling technique. The study found out that behavioral intention exhibits significant
and positive impact on the other variables used in the study. Medrad and Mohammadi
(2017) wrote on the impact of word of mouth on the adoption of mobile banking in
21
the main factor affecting mobile banking is the word of mouth. Patel and Patel (2017)
used structural equation modelling to examine the adoption of internet banking in
India and found that the increase in technology acceptance model inculcate higher
prediction compared to banking services technology acceptance model
Chaouali Yahia, and Souiden (2016) investigated the factors affecting customers’ intention in adopting internet banking services in Tunisia using partial least square and
SmartPLS as the estimation techniques. The results showed that the intention to adopt
online banking is influenced by trust, followed by other factors. Laukkanen (2016)
wrote on consumer adoption in relation to internet and mobile banking in Finland.
1736 consumers participated in the survey using logit regression model. The study
found that the value barrier mostly influences the adoption of online and mobile
banking. Szopiński (2016) studied the factors affecting the adoption of internet banking in Poland. Regression method was employed, and the findings revealed that
mortgages and credit cards mostly determine the impact of internet banking.
Montazemi and Qahri-Saremi (2015) examined the factors affecting online banking
adoption. The study employed two-stage random effects meta-analytic and structural
equation modelling methods, and it revealed that ten major factors affect consumer’s
adoption of the e-banking. Akhisar, Tunay and Tunay (2015) wrote on innovations on
the performance of banking using e-banking services as a case study in developed and
developing countries. Panel data analysis was used, and the report showed that bank
22
investigated the adoption of technology and consumers’ preference on online banking service in Nigeria using conjoint analysis. Their study found that the adoption of
e-banking services needed to increase some factors such as ATMs integrated with smart
phones, website customization, and biometric services. Shieh, Chang, Fu, Lin, and
Chen (2014) examined the factor that affects the adoption of mobile services in
Taiwan. Fuzzy hierarchy process model was used to analysis the gathered data and
they found that mobile service is important than both mobile equipment and
consumers' psychological factors.
Al-Smadi (2012) focused on the issues affecting the adoption of online banking in
Saudi Arabia. Multiple regression was used, and it found that uncertainty contributes
positively and significantly on ease and usefulness of e-banking. Mansumitrchai and
Chiu (2012) conducted a survey in UAE on internet banking adoption using analysis
of variance and reported that adopters and nonadopters differed on their attitudes
toward compatibility, trust and human contact.
Hernández-Murillo et al. (2010) studied the adoption of online banking strategy in US between 2003 and 2006 using panel form methods. They found out that bank-specific
features are the key elements in the adoption decision. Al-Somali, Gholami, and Clegg
(2009) wrote on the adoption of online banking behaviour in Saudi Arabia.
Questionnaires were distributed to 400 customers and partial least squares was used as
the technique. The findings revealed that internet connection, online awareness and
23
Yiua, Grantc, and Edgar (2007) studied the factors affecting the adoption of online
banking in Hong Kong. T-test and Pearson correlation were used as the estimation
techniques, and it was revealed that some factors showed positive connection with the
embracing of internet banking. Cheng, Lam, and Yeung (2006) examined internet
banking adoption in Hong Kong. They employed structural equation modelling as the
estimation technique and found out TAM model needs to be supported and extended
that what determine the behavior of the users is their intention. Shah and Siddiqui
(2006) investigated organizational factors in adopting online banking using Woolwich
bank in UK. The study employed interview form of qualitative research method, and
revealed some factors affecting e-banking, some of them are customers’
understanding, multiple channels, system integration, organizational flexibility, to
mention a few. Bauer and Hein (2006) studied risk effect on the adoption of online
banking in US, employing logistic regression as the estimation technique. However,
the findings showed that educating younger customers about internet banking risk is
more useful than educating older customers.
Table 1: Summary of Empirical Review Author(s) Name
and Date
Country Title Methodology
Rahia, Ghani and Ngah (2019)
Pakistan The acceptance and use of technology in banking adoption
Structural Equation Modelling Hamidi and
Safareeyeh (2019)
Iran M-banking effect on customer interaction and satisfaction.
Descriptive and regression
24 analysis Vetribvel, Rajini and Krihnamoorthy (2020)
India wrote on the effect service quality of online banking on consumer fulfillment in
Regression Analysis
Merhia, Hone, and Tarhini (2019)
Lebanese and British
The intention to use mobile banking services between
Lebanese and British consumers.
Structural Equation Modelling Alalwan, Baabdullah, Rana, Tamilmanic, and Dwivedic (2018) Saudi Arabia
The adoption of mobile internet in Saudi Arabia.
Structural Equation Modelling
Jehan and Ansari (2018)
Saudi Arabia
conducted a survey on the adoption of internet banking.
Descriptive Analysis Jansen and Schaik
(2018)
Netherlands Testing online behavior in banking sector Partial Least Squares Path Modelling Alalwana, Dwivedi, and Rana (2017)
Jordan The factors influencing the adoption of mobile banking by Jordanian bank Structural Equation Modelling Medrad and Mohammadi (2017)
Iran Impact of word of mouth on the adoption of mobile banking
Structural Equation Modelling Patel and Patel
(2017)
India Examine the adoption of internet banking in India Structural equation modelling Chaouali Yahia, and Souiden
Tunisia Factors affecting customers’ intention in adopting internet
PLSM and SmartPLS
25
(2016) banking services in Tunisia
Szopiński (2016) Poland Factors affecting the adoption of online banking in Poland
Linear Regression Laukkanen (2016) Finland Consumer adoption in relation to
internet and mobile banking
Logit Regression Montazemi and Qahri-Saremi (2015) US & Canada
the factors affecting online banking adoption. Two-stage random effects meta-analytic and structural equation modelling Akhisar, Tunay and Tunay (2015) Developed and developing Countries
Innovations on the performance of banking using e-banking services as a case study in developed and developing countries.
Panel Data Analysis
Dauda and Lee (2015)
Nigeria The adoption of technology and consumers’ preference on online banking service
Conjoint Analysis
Shieh, Chang, Fu, Lin, and Chen (2014)
Taiwan The factor that affects the adoption of mobile services in Taiwan. Fuzzy hierarchy process model Al-Smadi (2012) Saudi Arabia
Factors affecting the adoption of e-banking
Multiple Regression Mansumitrchai
and Chiu (2012)
UAE conducted a survey on internet banking adoption Analysis of variance Hernández-Murillo, Llobet, and Fuentes
US The adoption of online banking strategy
26 (2010) Al-Somali, Gholami, and Clegg (2009) Saudi Arabia
The adoption of online banking behaviour in Saudi Arabia.
PLS
Yiua, Grantc, and Edgar (2007)
Hong Kong the factors affecting the adoption of Internet Banking
T-test and Pearson correlation Cheng, Lam, and
Yeung (2006)
Hong Kong Internet banking adoption in Hong Kong
SEM
Shah and Siddiqui (2006)
UK Organizational factors in adopting e-banking using Woolwich bank in UK
Interview
Bauer and Hein (2006)
USA Risk effect on the adoption of internet banking
Logistic Regression Source: Writer’s Compilation (2019)
3.1.Gap in the Literature
This investigation attempts to focus on the factors affecting the adoption of internet banking services by civil servants in Cameroon. Meanwhile, the empirical reviewed above shows many investigations that have been conducted relating to the subject. However, this has not been majorly conducted in Africa continent where technology development is still the major focus in most of the countries.
27
4. MEHTODOLOGY
4.1.Research Design
Research layout involves planning and building inquiries to get answers to certain research questions. Research design requirements are practices and time-consuming nature that is often focused on the study question; directs the collection of information sources and styles; a structure setting out the relationship between the analysis variables and specifies the protocols for increasing test task. In the meantime, this study will use a systematic survey method to collect participant knowledge. The descriptive approach thus provides an objective description of persons, events or attributes, such as attitudes, views, skills, beliefs and awareness of a person, circumstance or community. The descriptive method is chosen, because it certifies a thorough explanation of the scenario and guarantees the lowest bias in knowledge collection.
4.2.Population
The study area is Cameroon which is at the central of Africa. More than 250 native languages are spoken in the country but has two official languages which are French and English. It has about 475,442km2 area with above 25.22million population according to World bank in 2018. Meanwhile, civil servants are the target audience of this study and its population according to payroll list as at 2018 is above 400,000 (Ngenge, 2019).
4.3.Sampling
Sampling notes the intention of collecting data from a survey which is to enable the researcher to make assertions about the population in which the sample is conducted
28
that focus entirely on the relationship between the target survey and the actual population. The sampling decision ought to be important in gathering the information needed. This study population is 400,000 participants though the total sample shall be selected using Yamane (1967) formula to arrive at the study sample population.
The formula is presented as:
𝑛 = 𝑁 1 + 𝑁(e)2 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 𝑛 = 𝑜𝑣𝑒𝑟𝑎𝑙𝑙 𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑎𝑝𝑙𝑒 𝑁 = 𝑃𝑜𝑝𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑒 = 𝐿𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑙 𝑜𝑓 𝑠𝑖𝑔𝑖𝑛𝑖𝑓𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒 (𝑇𝑎𝑘𝑒𝑛 𝑡𝑜 𝑏𝑒 0.05) 𝑛 = 𝑁 1 + 𝑁(e)2 = 400000 1 + 400000(0.05)2 = 399 𝑛 = 393 Respondents
Three hundred and ninety-nine (399) questionnaires shall be used and distributed in the study. The respondents shall be selected randomly from different location of the Cameroon.
4.4.Validity
The validity of this thesis is based on three elements, such as face validity, text validity and validity model. This thesis will carry out the three validity checks where factor analysis will be used for the validity of the design, the pilot sample will be used for the validity of the face while the validity of the material will be applied to the contents of the subsequent studies to determine the inquiries.
29 4.5.Reliability
This entailsto the degree in which the scale measurement produces reliable results. To ensure instrument reliability in this study, the study instrument will be subjected to different testing techniques, however, the instrument shall be distributed to the employees of the banks in Cameroon, response will be analyzed using coefficient alpha, and a coefficient above 0.5 is considered reliable.
4.6.Research Tool
This research would be using quantitative processing techniques. The quantitative approach involves the analytical data collection by means of a questionnaire administered to the target group. The questionnaires shall be built using the ranking system of the binary answers like Yes or No and Likert such as strongly agree, agree, neutral, disagree, and strongly disagree. The construct validity of the research instrument will be submitted to factor-analysis using principal component analysis with varimax rotation. The participants' comments will be evaluated using alpha coefficient, and a Cronbach Alpha coefficient above 0.6 is considered accurate based on the thumb rule. Correlation and Regression analyses shall be used to attain the study's basic objectives and general objective.
4.7.Model Specification and Framework
This study shall adapt a functional model which is presented as follows:
OBS = f(IF, STF, CSA, AF, U)
Where
OBS – Online Banking Service
IF – Innovative Factor
STF – Security & Trust Factor
30 AF – Awareness Factor
U – Other Factors
4.8.Conceptual Framework
Independent Variable Dependent Variable
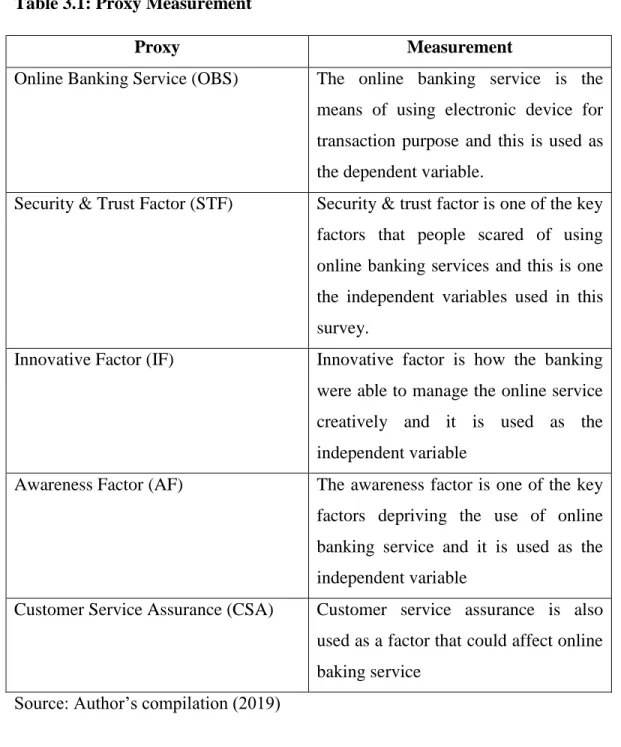
Source: Author’s Design
This study independent variable is the key factors which is proxy with security & trust factor, innovative factor, awareness factor, and customer service assurance while the dependent variable is online banking service.
Innovative
Factor
Awareness
Factor
Security & Trust
Factor
Online Banking
31 4.9.Description of Proxy
Table 3.1: Proxy Measurement
Proxy Measurement
Online Banking Service (OBS) The online banking service is the means of using electronic device for transaction purpose and this is used as the dependent variable.
Security & Trust Factor (STF) Security & trust factor is one of the key factors that people scared of using online banking services and this is one the independent variables used in this survey.
Innovative Factor (IF) Innovative factor is how the banking were able to manage the online service creatively and it is used as the independent variable
Awareness Factor (AF) The awareness factor is one of the key factors depriving the use of online banking service and it is used as the independent variable
Customer Service Assurance (CSA) Customer service assurance is also used as a factor that could affect online baking service
32 4.10. A-priori Expectation
The expression of the a-priori is represented as; ∂OBS
∂STF > 0, Security & Trust Factor is expected to be positive to online banking service ∂OBS
∂IF > or < 0, Innovative Factor is expected to be either positive or negative to online banking service.
∂OBS
∂AF > 0, Awareness Factor is expected to be positive to online banking service. ∂OBS
∂CSA > or < 0, customer service awareness is expected to be either positive or negative to online banking service.
33 5. DISCUSSION OF ANALYSIS
5.1.Demographic and Descriptive Analyses
Table 4. 1: What is your sex group?
Freq %
Male 165 53.6
Female 143 46.4
Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Figure 1: sex of participants Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 4.1 and figure 1 shows the category of the participants by sex and revealed that 165 of them with 53.6percent are male while the remaining 143participants representing 46.4percent are female, connoting that the variation between male and
34
female that participated in this study is close though there was no form of discrimination between male and female during the distribution exercise.
Table 4. 2: What is your age?
Freq % Under 18 24 7.8 19-25 120 39.0 26-35 104 33.8 36-45 60 19.5 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Figure 2: Age of the participant Source: Researcher’s computation
The report shows that the participants age bracket below 18 is 24 representing 7.8percent, age bracket between 19-25 has 120participants with 39.0percent, age between 26-35years has 104 participants representing 33.8percent while age between 36-45 has 60 participants with 19.5percent, indicating that the age bracket between 19-25 has the higher participants, followed by age between 26-35, 36-45 and under 18years respectively.
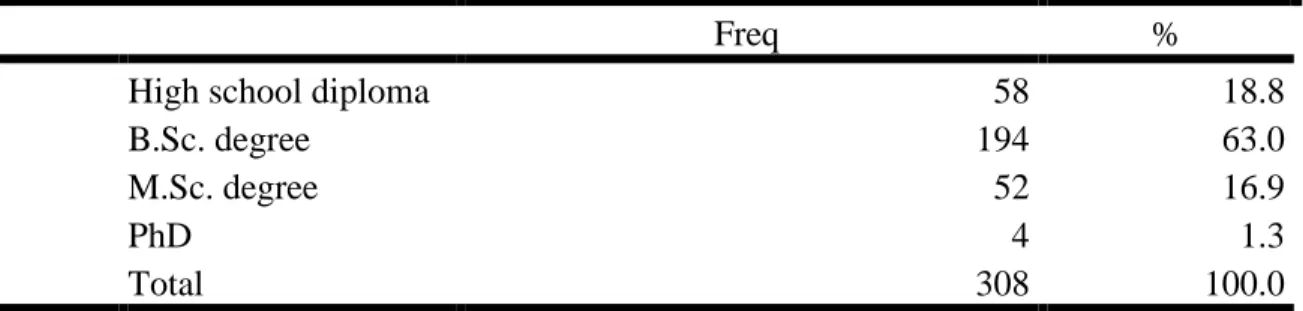
35 Table 4. 3: What is your qualification?
Freq %
High school diploma 58 18.8
B.Sc. degree 194 63.0
M.Sc. degree 52 16.9
PhD 4 1.3
Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Figure 3: Qualification of the Participant Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 4.3 and figure 3 show that 58 participants with 18.8percent have higher school diploma, 194 of the participants with 63.0percent have B.Sc certificate, 52 participants with 16.9percent have masters’ degree while 4 of the with 1.3percent have doctoral degree, implying that most of the participants have bachelor’s degree, followed by higher school diploma, masters and doctoral certificates.
36 Table 4. 4: What is your marital status?
Frequency Percent
Single 84 27.3
Married 222 72.1
Widow 2 .6
Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Figure 4: Marital status of the participant Source: Researcher’s computation
The table and figure display that 84participants indicating 27.3percent are single, 222 participants with 72.1 are married while 2 participants with 0.6percent are widow, indicating that many of the respondents are married followed by single and widow respectively.
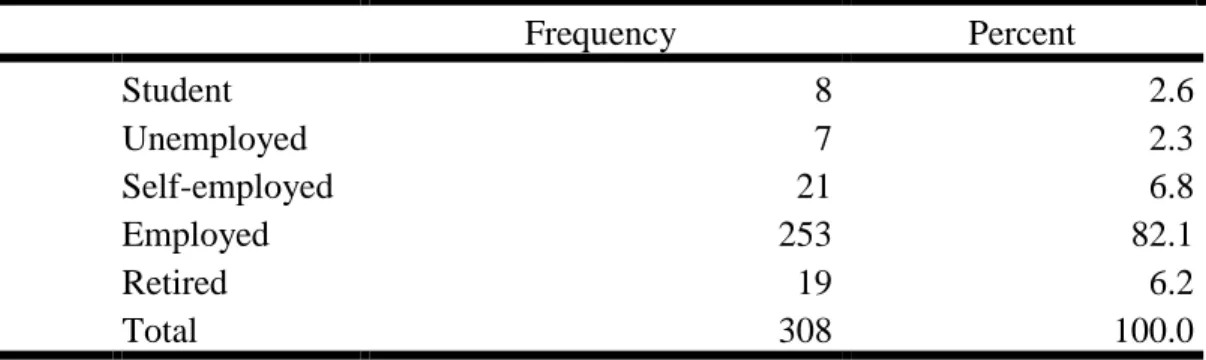
37 Table 4. 5: What is your employment status?
Frequency Percent Student 8 2.6 Unemployed 7 2.3 Self-employed 21 6.8 Employed 253 82.1 Retired 19 6.2 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Figure 5: Employee Status Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 4.5 and figure 5 show the employee status of the participants. 8 of them with 2.6percent are student, 7 of the participants representing 2.3percent are unemployed, 21 participants with 6.8percent are self-employed, 253 of them representing 82.1percent are employed while 19participants with 6.2percent are retiree. This implies that the higher participants are the employed participants followed by self-employed, retiree, student and unemployed respectively.
38 5.2.Frequency Result
Table 4. 6: Do you use online banking services?
Freq %
No 16 5.2
Yes 292 94.8
Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
16 of the participants representing 5.2percent chose No that they do use online banking services while 292participants with 94.8percent chose Yes, indicating that most of the participants use online banking services.
Table 4. 7: Online services have truly changed the banking structure in Cameroon Frequency Percent
No 20 6.5
Yes 288 93.5
Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 7 shows participants view about online services have truly changed the banking structure in Cameroon, 20 participants with 6.5percent chose No while 288 participants representing 93.5percent chose Yes, implying that majority concur that online services have truly changed the banking structure in Cameroon.
Table 4. 8: The interaction of online banking service is
Freq % Poor 21 6.8 Fair 270 87.7 Good 15 4.9 Very good 2 .6 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation Table 4.8 presented the interaction of online banking service and 21 participants representing 6.8percent chose poor, 270participants with 97.7percent chose fair, 15participants representing 4.9percent chose good while 2 participants chose very good, indicating that the online banking service interaction in Cameroon is fair.
39 Table 4. 9: Online transaction service is
Frequency Percent Poor 23 7.5 Fair 254 82.5 Good 29 9.4 Very good 2 .6 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
23 participants with 7.5percent chose that online transaction is poor, 254 participants with 82.5percent chose fair, 29participants with 9.4percent chose good while 2participants with 0.6percent chose very good. This indicates that online transaction is fairly operates in Cameroon.
Table 4. 10: Information content of the online banking service is
Frequency Percent Poor 29 9.4 Fair 137 44.5 Good 140 45.5 Very good 2 .6 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 4.10 presented the information content of the online banking service and 29 participants representing 9.4percent chose poor, 137participants with 44.5percent chose fair, 140participants representing 45.5percent chose good while 2 participants chose very good, indicating that information content of the online banking service in Cameroon is fairly good.
40
Table 4. 11: The awareness of the online banking service is
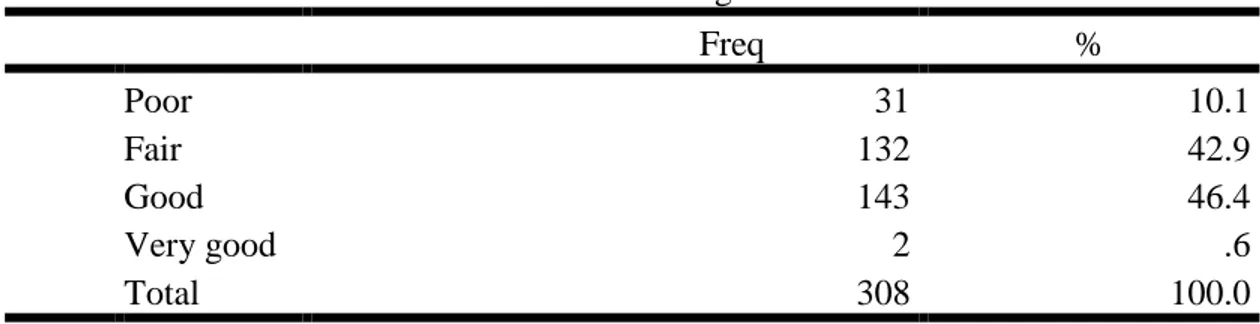
Freq % Poor 31 10.1 Fair 132 42.9 Good 143 46.4 Very good 2 .6 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
31 participants with 10.1percent chose that the awareness of the online banking service is poor, 132 participants with 42.9percent chose fair, 143participants with 46.4percent chose good while 2participants with 0.6percent chose very good. This indicates that the awareness of the online banking service is fairly good in Cameroon.
Table 4. 12: The quality of the service is
Freq %
Poor 34 11.0
Fair 259 84.1
Good 15 4.9
Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 4.12 presented the quality of the service and 34 participants representing 11.0percent chose poor, 259participants with 84.1percent chose fair, while 15participants representing 4.9percent chose good, indicating that the quality of the service is fair.
Table 4. 13: Internet banking is difficult to understand and its time consuming
Freq % Strongly agree 49 15.9 Agree 224 72.7 Neutral 14 4.5 Disagree 18 5.8 Strongly disagree 3 1.0 Total 308 100.0
41
49 participants representing 15.9 percent strongly agreed that internet banking is difficult to understand and its time consuming, 224 of the participants representing 72.7percent agreed, 14participants representing 4.5percent are neutral, 18 of them representing 5.8percent disagreed while 3 participants representing 1.0percent strongly disagreed. This connotes that internet banking is difficult to understand and its time consuming among many of the users.
Table 4. 14: Internet fraud discourages the use of internet banking
Frequency Percent Strongly agree 62 20.1 Agree 201 65.3 Neutral 11 3.6 Disagree 23 7.5 Strongly disagree 11 3.6 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 4.14 shows the respondents report on whether internet fraud discourages the use of internet banking and 62participants indicating 20.1percent chose strongly agree, 201participants with 65.3percent chose agree, 11 of them with 3.6percent chose neutral, 23participants representing 7.5percent chose disagree while 11participants with 3.6percent chose strongly disagree, which indicates that internet fraud discourages the use of internet banking in Cameroon.
Table 4. 15: Dissemination of information through the internet is secure and efficient Freq % Strongly agree 10 3.2 Agree 19 6.2 Neutral 18 5.8 Disagree 257 83.4 Strongly disagree 4 1.3 Total 308 100.0
42
10 participants representing 3.2percent strongly agreed that dissemination of information through the internet is secure and efficient, 19 of the participants representing 6.2percent agreed, 18participants representing 5.8percent are neutral, 257 of them representing 83.4percent disagreed while 4 participants representing 1.3percent strongly disagreed. This connotes that dissemination of information through the internet is not that secure and efficient.
Table 4. 16: Using internet banking is difficult for the older customers so, they mostly go against online banking
Frequency Percent Strongly agree 63 20.5 Agree 187 60.7 Neutral 26 8.4 Disagree 21 6.8 Strongly disagree 11 3.6 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 4.16 displays the partakers report on whether using internet banking is difficult for the older customers so, they mostly go against online banking and 63participants indicating 20.5percent chose strongly agree, 187participants with 60.7percent chose agree, 26 of them with 8.4percent chose neutral, 21participants representing 6.8percent chose disagree while 11participants with 3.6percent chose strongly disagree, which shows that using internet banking is difficult for the older customers so, they mostly go against online banking in Cameroon.
Table 4. 17: Online banking is not reliable as the traditional form of banking
Frequency Percent Strongly agree 52 16.9 Agree 205 66.6 Neutral 23 7.5 Disagree 22 7.1 Strongly disagree 6 1.9 Total 308 100.0
43
52 participants indicating 16.9percent strongly agreed that online banking is not reliable as the traditional form of banking, 205 of the participants representing 66.6percent agreed, 23participants representing 7.5percent are neutral, 22 of them representing 7.1percent disagreed while 6 participants representing 1.9percent strongly disagreed. This connotes that many of the participants supported that online banking is not reliable as the traditional form of banking.
Table 4. 18: The quality of services rendered through e-banking encourages customers’ patronage and loyalty
Freq % Strongly agree 12 3.9 Agree 18 5.8 Neutral 24 7.8 Disagree 254 82.5 Total 308 100.0
Source: Researcher’s computation
Table 4.18 reveals the respondents report on whether the quality of services rendered through e-banking encourages customers’ patronage and loyalty, and 12participants indicating 3.9percent chose strongly agree, 18participants with 5.8percent chose agree, 24 of them with 7.8percent chose neutral, while 254participants representing 82.5percent chose disagree, indicating that the quality of services rendered through e-banking does not encourages customers’ patronage and loyalty.
Table 4. 19: Online interaction with the banking services require a lot of mental effort and this discourage some customers
Freq % Strongly agree 60 19.5 Agree 194 63.0 Neutral 25 8.1 Disagree 26 8.4 Strongly disagree 3 1.0 Total 308 100.0