Selçuk J. Appl. Math. Selçuk Journal of Vol. 8. No.2. pp. 37 - 47 , 2007 Applied Mathematics
Automotive Business with Foreign Capital in Turkey and an Econo-metrics Application
Haldun Soydal and Serdar Altınok
Faculty of Economics and Administrative Sciences, Department of Economics Policy A.Keykubat Campus 42075 Konya/Turkey;
e-mail:hsoydal @ selcuk.edu.tr,saltinok @ selcuk.edu.tr
Received : June 28, 2007
Summary. In Turkey, among the business with foreign capital which work-ing order automotive sector has an important place. Since automotive business with foreign capital are big companies that can be essential to Turkey’s prob-lems in terms of macroeconomics. These businesses are highly profitable for Turkey’s economy in terms of employment, manufacture and export. Therefore, automotive business with foreign capital which are important are studied as an empirical study among their income, exchange rate, production, employment with the help of an econometrics analysis.
Key words:Econometrics analysis, automotive, granger, export, VAR model, production.
1. Introduction
Due to the globalization, foreign direct investment has been increased very rapidly and reaches 1 billion $ volume totally in the world and also very impor-tant for Turkey. It is anticipated that Turkey should pull 30 and 50 billion $ foreign direct investment annually due to the FIAS report in respect of its huge internal market and location. In recent years, although 20 billion $ has been directed by the help of privatization, this amount is not enough for high ex-pectations. Because Turkey needs much amount of foreign direct investment in case increasing current account deficit has been resolved. In this study, not only the effect of foreign direct investment over export ratio and its trends has been evaluated but also some inferences has been conducted by Granger econometric test.
2. Development of World Automotive Sector
Automotive sector can be defined as a branch of industry that manufactures road vehicles which make up needs of a country such as cargo and carrying. Be-sides, automotive sector is a locomotive sector that manufactures road vehicles by creating demand for supplier industry such as from steel to glass, from rubber to electronic parts. Automotive sector which has over five-hundred-years past was on the process of establishment by French Cugrot between 1769- 1771. The biggest ten manufacturing firm in the manufacturing vehicle world; General Motors, Toyota, Ford (Jaguar-Volvo), Volkswagen Gruppe, Daimler-Chrysler, PSA Peugeot-Citroen, Honda, Nissan, Hyundai-Kia, Renault-Dacia-Samsung classified like this. These firms produce %77 of manufacturing motor vehicle. If information of 2005 is taken into consideration, it can be said that %71 of trans-portations are exported. Volkswagen which is the leader of automobile bazaar in Europe increased its market share in 2005 with 2.745 sales figures, although it was %18.1 in 2004. While the market share of Ford decreases from %11.2 to %10.9, Toyota increases its market share to %53 and Renault’s share decreases from %10.3 to %9.8. In Europe 2.2 millions of people are working in automotive sector, and this number is equal to the %6 of total employment.1Because of the
high level of labour cost and developed union rights manufacturers gravitate to the east countries where cost is lower.
Table 2. 1. World of Motor Vehicle Bazaar (1000) *Sources: Automotive Industry Association, Access:
http//www.osd.org.tr, Access Date: 13.03.2006
As it is seen in the table there is a great increase in demand in Southeast Asia in 2005 in the sales of transportation vehicles. Malaysia % 15, Indonesia %13, Thailand %12, Philippines %10 increases their sales. Asian countries that in-crease the production rate parallel to the sales produce the %9.7 of universal
production. In People’s Republic of China which is one of the most impor-tant investment countries, manufacturing of transportation vehicles reaches 5.3 million.
Table 2. 2. World Automobile Production (1000) *Sources: Automotive Industry Association, Access:
http//www.osd.org.tr, Access Date: 13.03.2006
Total 64.7 million motor transportation vehicles produced in 2005. In table 2.2 world automobile production %11 increased in the last 4 years, automo-bile production increase in the developing countries is %54, and their share of world production increased from %15 to %20.6. Share of turkey in the world automobile production increased from %0.4 to %1.
3. Development of Turkish Automobile Sector
Because there was no automotive sector during the years of establishment of Republic, demands for limited motor vehicles responded with the help of ex-port. .In those years railway transportation was mostly applied; thus, it limited the demand for motor vehicles. During Post World War II era, because of the developing international relations with the western countries highway network system was started to establish. In 1954 the montage permission was given to Willys Overland Co and it became the starting day of automotive sector. After that Uzel, BMC, Otosan, Chrysler, Genoto, MAN and Otoyol followed the same way. Until 1990 each produced vehicle contributed much too Turk-ish automotive supplier sector. During 90s, some precautions were taken and investments for new and modern vehicles were encouraged in order to make au-tomotive sector bring foreign currency to the country. High production quality and low prize of production were the main attraction point for the significant automotive production companies and made them invest money on this sector in turkey. By the end of 90s turkey became one of the automotive production centres due to its close geographical position to Europe and its high potential for production.2
3.1. The Statue of Automotive Sector in Turkey’s Economy
In our country, demand for motor vehicles in bazaar is mostly affected from the instability in economical and social life. Since 60s, the establishment of automotive industry in Turkey has been in close relationship with EU. Tariff
union in 1996 gave way to the new opportunities in market, together with goods in free circulation and liberalized imports, and competition level in local market increased. In this process, automotive intuitions in Turkey gained a position which can produce for the foreign markets. .
In Turkey the position of the automotive industry has great differences between its position at the beginning and today. Turkey is a country which produces competitive automotive products to the global markets that are in the same geographical region and has that industry. Because of this reason, Turkey is in the path of EU’s expanding global automotive industry, as it is stated in the 8th five-year-growth-plan, automotive industry in Turkey.3
Turkish automotive industry has a great significance in Turkish production in-dustry. Production in automotive industry is based on mostly exporting since the demand in the country is lower than the supply. In Turkish automotive market the number of the automobiles and commercial vehicle sold are: 765,651 in 2005, 740,233 in 2004, and 392,900 in 2003.
Although Turkish automotive sector does not have a long history, it has shown a great development and now it is the second great industry and since 2005 it has realized 11.693.388.825 $ exportation. As it is shown in table 3.1.1, the increase tendency between 2001 and 2005 is analysed, it is seen that %49, 84 average range is calculated.4
Table 3. 1. 1 Exportation of Automotive Supplier Industry according toYears Sources: Automotive Industry Association, Access:
http//www.osd.org.tr, AccessDate: 13.03.2006
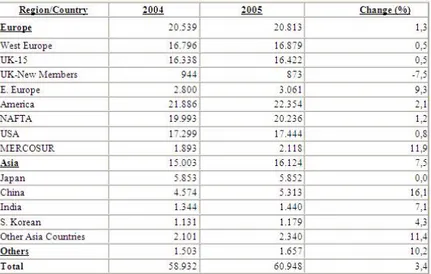
Automotive basic industry developed and increased its exportation especially in the last five years together with the investments such as: R&D, coordination with the supplier industry, employment of qualified labour force. Every passing year automotive sector which increases the production and its exportation has great increases in the large parts of the products. Turkish automotive sector, the leading developed western countries in 2005, export traded to 177 countries in the 5 continents and to 15 self-governing territory. %68 of total automotive exportation implemented to 25 EU-member countries which were the biggest commercial partners. The exportation to Germany, Italy, France, England and Spain consisted of $6.448.822 and the half of the total exportation. In recent years, our country has been regarded as an attractive investment area especially by the Middle Eastern countries. Exportation of basic industry showed hardly any changes among the groups of countries.
Exportation of basic industry concentrated on the UE’s countries in 2005 as it was in 2004. The most important increase was experienced in the exportation that gravitated Middle East. . In 2004 it covered %4.8 of basic exportation,
and this number became %7.3 in 2005. The biggest share in basic exportation is UE’s countries with this number: $6.295.110.056. This amount of exportation $741.143.445 was invested to Eastern Block that was the second. While old Eastern Block is the third in commercial exportation, countries in Africa are the fourth in size as a commercial market. The only country which experience decrease is Turkish Republic.
Table 3. 1. 2 Exportation among Firms (Per-Production) Sources: Automotive Industry Association, Access:
http//www.osd.org.tr, AccessDate: 13.03.2006
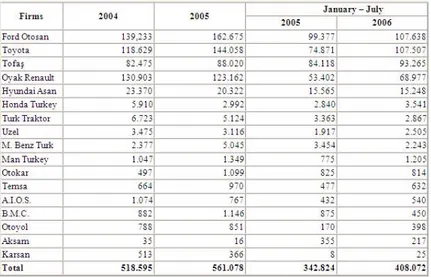
As it is asserted in the table, as it was in exportation in 2004 Ford Otosan had the first rank with hierarchy with 162.675, and Toyota followed it with 144.058. Oyak Renault, Tofa¸s, Hyundai Assan had again the first rank in exportation. Ford Otosan achieved 107.638 number of exportation in the first seven months in 2006, as it was in the same months in 2005, in the same term Toyota fol-lowed it the number of 107.507. The exportation rate of Tofa¸s did not show any noticeable changes. According to these results it can be concluded that automotive firms with foreign capital have significant place in the sector.
Table 3. 1. 3 The list of the 10 Countries according to Export Rates and Free Zone Sources: Automotive Industry Association, Access:
According to table 3.1.3 among the countries that we export Germany the first rank with $148.494 and Italy follows it with $140.068. France, England and Spain are the countries which we export. Since 2003, when developing import rates analysed, it can be seen that there is no noticeable change in the rate of import.
Table 3. 1. 4 Rates of Automotive Industry Importin 2003/2006 Sources: Automotive Industry Association, Access:
http//www.osd.org.tr, AccessDate: 13.03.2006
In 2003 the rate of import was first $400.711, in 2004 it became $745.812 and in 2005 it reached $763.186. In the first seven months in 2006, total $392.108 imported (Table 3.1.4).
If we are supposed to analyse the rates of export and import according to foreign commerce, when included the related industry products of the sector, the tendency of the balance level is negative.
That the sector mostly gravitated to export in 2001 and 2002, a stage of recession and to get narrow the internal in these years market based import decrease leads to surplus. One of the structural problems of sector is the rate especially in automotive area %70 and %43 in soft commercial vehicle market. In order to follow developed technology global firms they are making new models or making modifications on previous models each year on marketing these models both World’s market and Turkey’s market. Together with Customs Union, the market is under the influence by these firms. In Turkey, in total, 38 import labels are sold. Another structural matter is investments of new models in our country need import entry. The rate of using import entry is increase when it is in the process of production. The increase in the number of import automobile and abounded of trend marks at the same time increases the rate of the import; the sector related to the renewal of these vehicles increases import. Because of this reason, on the basis of external deficit which is given there are products of supplier industry. In 2003, this external deficit was -$1250.5
In automotive basic industry, direct employment was became 33.145 people in 2003. Although, especially in the time of crisis, the production rate decreases in a great deal, in order to protect labour force all the necessary precautions are taken. In sector, the reason for cost to grow high quality labour force for competition, and, apart from other sectors, in this sector the continuance of labour force is principal cause.6
In automotive supplier industry it is estimated that employment rate is about 100.000 people and in supplier industry it is about 500.000 people. Moreover, it can be concluded that because of the butterfly effect of this industry in low
material industry, marketing service, department of the spare parts, the number of working people are about 795.000.
4. The Application of Granger Causality Test for the Var Model of Production, Employment, GDP and Exchange Rate in the Automo-tive Sector
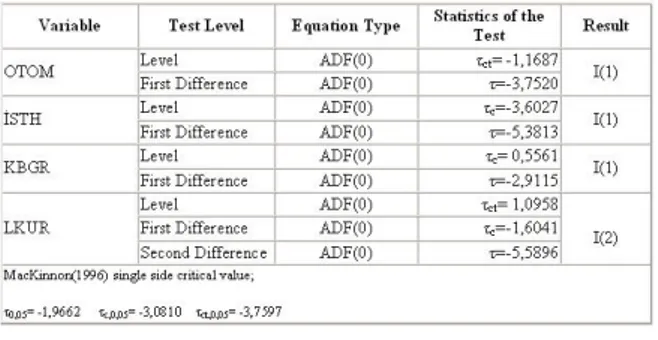
In empirical analysis, firs,t variables were analyzed if they stable or not, then Granger causality test was applied for the VAR model. In the third step, depend on the VAR model; stimulus and response analyses of variables are done. In this study, automobile production in 1990-2006, the number of employment, income and exchange rate are taken into analyze per year. These data are based on the information gathered from the sources of Central Bank (EVDS), and the data sets of State Planning Organization. In the given model, the exchange rate variable and the time set shows an increase; thus, logarithm is taken into consideration. The application of the Unit Root test showed that the differences between exchange rate variable and others are static.
Table 4. 1. The results of the unit root test
After fixing the variables in a certain level it is necessary to sort the variables of the Var analysis. In this process the Granger causality test is applied.
According to the causality test results the rank of the variables from external to internal for the VAR analysis is as D˙ISTH, DKBGR, DDKUR and DOTOM. Var model which has minimum retardation speed is used without auto corre-lation in the analyse. Also, according to the graph1, var model’s roots which provide invisible an effect reaction analyse, appear a unity of circle.
Graph 4. 1. Characteristic Roots
LM test is made for auto correlation of remaining in model.According to the picture 19 auto correlation doesn’t become comfortable. White exchange variant test which is not used crossing term for different variant doesn’t meet by chance a different variant.
Table 4. 3. Autocorrelation LM Test
Graph 4. 2. Automobile production reaction in the employment, quota per capita and rate of exchange
Graph4.2.The reaction of the automotive production to one unit standard devi-ation shock in the employment, per capita income and exchange rate variables are indicated. While automobile production gives positive reaction dependent upon employment increase at the first term, it gives negative reaction at the second term and it becomes less violence of reaction at the last terms.
Automobile production gives positive reaction in the unit of increase in the per capita income and this process reaction continue five terms approximately. The-oretically, when exchange rates increase, automotive production gives negative reaction in the first term but this reaction’s ratio is low showed in Graph 4.2.
Table 4.5Automobile Production Variant Decomposition Table
According to the graph, the most important thing is employment level in the automobile production .While explanatory reaction of employment level is %68 proportion at the first term,this reaction materialize %57 proportion in ten terms. While personal earnings level explains %18 of automobile level at the first term, it explains %32 at the fourth term.Explanatary effect of rate of ex-changes are defeated %1 level in the acceptable terms.While retadation values of automobile production is %12.8 level at the first term, it decreases %9 level at the second term and there is not important exchange at the last terms.Finally we can say that the most important factor is employment level in the automobile production and the second important exchange is earnings level.
4. Result
In Turkey foreign capital automotive business administrations have important generosity inside the foreign capital administrations and existent effects as(in point of) production,employment, exports, technology contribution for Turkey economy then Granger causality test become adapted for VAR model.At the third stage, according to the Var model , effect reaction analysis of changable and variant decomposition are made. Finally it is found that,earnings augmen-tation is cause of automobile production and rate of exchange augmenaugmen-tation reduces production with negative effect and it is proved that the first important factor is employment level and the second one is earnings level in automobile production.
Acknowledgement
This paper studied by the help of the Ph. D. Thesis of Haldun Soydal consulted by Prof Dr. Serdar Altınok called “Efficiency Analysis of Direct Foreign Invest-ment in Turkey: The Case of Automotive” and supported by Selcuk University Scientific Researh Project Fund numbered 07103009
References
1. ARIMAN Abdurrahman, Foreign Direct Investment in Turkey , YASED Publica-tions, ˙Istanbul, 2001.
2. BENDE-NABENDE Antony, Globalisation, FDI and Sustainable Devolopment: Theory, Evidence and Policy, Ashgate Publishing Ltd, England, 2002.
3. CALVET A.L., A Synthesis of Foreign Direct Investment Theories and Theories of The Multinational Firm, Journal of International Business Studies, 1981
4. ˙Istanbul Chamber Of Industry , Foreign Direct Investment and Turkey, ˙Istanbul, 2002
5. DÜNDAR Mehmet, General view of Turkish Automotive Industry, The effects of Custom Union on Industry and The Situation of Foreign Capital in Industry, ,1995. 6. ORHAN Osman,T he Competitive Power of Turkish Automotive and Automotive Components Industry During Process of Custom Union, ˙Istanbul Chamber of Com-merce Publications, 1996.
7. Automotive Manufacturers Assocation, Foreign Trade of Automotive Industry 1992-2003, 2004.
8. GÜLE¸S H.Kür¸sat, The Impact of Advanced Manufacturing Technologies on Buyer-Supplier Realionships in The Turkish Automotive Industry, The University of Leeds School of Business and Economic Studies, 1996.
9. KARABULUT Tahsin, Turkish Automotive Industry Economics Structure and Automotive Demand Analysis (1980-2000), Doctorate Thesis , Selcuk University Social Science Institute, 2002.
10. ˙Istanbul Chamber Of Industry, Foreign Direct Investment and Turkey , ˙Istanbul 2002.
11. ˙Istanbul Chamber Of Industry , Foreign Direct Investment and Turkey: Strategy Plan, 2002.
12. ˙Istanbul Chamber of Commerce, Economics Report, ˙Istanbul, December 2003. 13. Central Bank of The Republic of Turkey, Annual Report , 2006.
14.http//www.osd.org.tr
15.http//www.iso.org.tr
16. H. Soydal, “Efficiency Analysis of Direct Foreign Investment in Turkey: The Case of Automotive Industry ”, Ph. D. Thesis , Selcuk University Social Science Institute, 2007.