030
Effects of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy on Systemic Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Galectin-3 Level in Heart Failure
Hikmet Yorgun1, Hamza Sunman1, Ugur Canpolat1, Ahmet Hakan Ates2, Levent Sahiner1, Ergun Barıs Kaya1, Kudret Aytemir1, Ali Oto1;1Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey; 2Samsun Mehmet Aydın Training and Research Hospital, Samsun, Turkey
Aim:To investigate the long term effects of CRT on systemic inflammation, ox-idative stress and galectin-3 level in heart failure patients. Methods and results: In 50 heart failure patients (NYHA II, III-IV), we evaluated interleukin-6, high sen-sitive C-reactive protein, myeloperoxidase, uric acid, total bilirubin and galectin-3. Following CRT implantation, patients were evaluated at twelfth months with echo-cardiographic evaluations defining responders by a 15% reduction in end-systolic volume. In addition, New York Heart Association class, distance of 6-min walk, the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure questionnaire, B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) were measured before and 6 months after CRT. Twenty-two of 32 patients (71%) responded to CRT. The responder group demonstrated significant decrease in BNP level from 403671 to 227640 pg/ml, p50.007; in NYHA class from 2,860,3 to 2,260,3, p50,044 paralleling the clinical improvements. Namely, re-sponder patients showed greater improvement in the 6-min walk test (from 286658 to 305665m, p50,001) and the Minnesota score (from 3867,6 to 3467,4 points, p50,001) than non-responder patients at 1 year. Levels of MPO was significantly decreased in responder group [21,9 ng/ml (75,7-84,4) vs. 11,8 ng/ml (0,9-18,4), p50,001]. Levels of MPO was significantly decreased and level of uric acid, level of total bilirubin was significantly increased in non-responder group [33,0 ng/ml (0,9-99,1) vs. 10,1 ng/ml (2,4-16,9), p50,040; 5,8261,93 mg/ dl vs. 7,2562,25 mg/dl, p50,030; 0,6160,23 mg/dl vs 0,9260,45 mg/dl, respec-tively]. Level of interleukin-6, high sensitive C-reactive protein and galectin-3 were not significantly changed in both group of responder and non-responder pa-tients. Conclusion: It was showed that CRT improves oxidative stress in responder heart failure patients. However, CRT did not significantly reduce level of systemic inflammation markers and level of galectin-3 in responder or non-responder patients.
031
Ischemia-Modified Albumin Levels in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure Treated with Dobutamine or Levosimendan: IMA-HF Study Yuksel Cavusoglu1, Sule Korkmaz2, Selda Demirtas2, Erkan Gencer3, Hatice Sasmaz4, Fezan Mutlu1, Mehmet Birhan Yilmaz5; 1Eskisehir Osmangazi University, Eskisehir, Turkey; 2Ufuk University, Ankara, Turkey; 3Kilis Public Hospital, Kilis, Turkey; 4Ankara Yuksek Ihtisas Hospital, Ankara, Turkey; 5Cumhuriyet University, Sivas, Turkey
Purpose:Ischemia-modified albumin (IMA) is a very sensitive biomarker of myo-cardial ischemia before necrosis. IMA has also been found to be elevated in the setting of oxidative stress, acidosis, hypoxia, inflammatory state and sodium and calcium pump disruptions which are also involved in the pathophysiologic process of heart failure (HF). However, data about IMA levels specifically in patients with HF are still lacking. Dobutamine (DOB) is known to increase oxygen consumption, and thereby may precipitate ischemia and myocyte damage. In contrast to DOB, levosimendan (LEVO) does not increase myocardial oxygen demand and therefore is thought to have cardio protective properties. So, we aimed to evaluate 1-) serum IMA concentrations in acute decompensated HF and 2-) the effects of DOB and LEVO treatments on IMA levels. Methods: This prospective multicenter study was performed at the five independent sites. Fifty-nine patients admitted to par-ticipating centers with clinical signs and symptoms of NYHA III-IV acute decom-pensated HF and LVEF !35% were enrolled in this study. Blood samples for IMA measurements were obtained from all patients at baseline and 24 h after the initiation of HF therapy. 18 patients were treated with guidelines-recommen-ded HF therapy with oxygen, diuretic, vasodilators (control group), 18 received an additional 24-h infusion of LEVO with a loading dose of 12mg/kg over 10 min followed by a continuous infusion of 0.2mg/kg/min (LEVO group) and 23 had DOB treatment with a continuous infusion of 10mg/kg/min for 24-h in ad-dition to optimal pharmacologic therapy (DOB group). A single serum specimen was also collected from 32 apparently healthy individuals. IMA concentrations were measured by albumin cobalt binding colorimetric assay and results were given as absorbance units (AU). Results: In patients with acute decompensated HF, mean serum concentration of IMA was found to be significantly higher than those of apparently healthy population (0.89460.23 AU vs 0.37960.08 AU, p ! 0.0001). Overall, IMA levels significantly decreased after 24-h of the initiation of appropriate HF therapy (0.89460.23 AU and 0.83260.18 AU, p !0.013). Fur-thermore, IMA levels were also found to significantly decrease in control group (1.04160.28 vs 0.88460.15 AU, p!0.041), in LEVO group (0.77160.18 vs 0.72860.18 AU, p!0.046) and also in DOB group (0.89260.18 vs 0.82060.13 AU, p!0.035). Conclusions: This study suggested for the first time that patients with acute decompensated HF had elevated levels of IMA and appropriate HF ther-apy significantly reduced serum IMA levels. The findings of this study also demon-strated that both DOB and LEVO treatments did not increase in IMA levels, suggesting lower potential in inducing myocardial ischemia when used in recom-mended doses.
032
Corin Levels Are Linked to Systolic Function and Serum Sodium
Ryan D. Ward, Syed S. Zaidi, Kodangudi Ramanathan, Xinhua Yu, Inna P. Gladysheva, Guy L. Reed; University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, TN
Introduction:Biomarkers have great diagnostic and prognostic value in heart failure (HF). Patients with left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) and HF have elevated levels of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and brain natriuretic peptide (BNP). Our previous studies indicate that levels of corin, a heart enzyme that activates pro-ANP and pro-BNP, are depressed in patients with HF. These findings suggest that corin may be a useful biomarker with functional significance. Hypothesis: We hy-pothesized that plasma levels of corin were linked to LVSD and HF. In this study, we explored this relationship as well as the association of corin with other clinical variables. Methods: In this prospective study of male veterans (ages 50-70, N548), we examined clinical data and corin levels in 3 groups: control patients with normal ejection fractions (EF 6363%, N516), LVSD with HF patients (EF 2468%, N516) and LVSD without HF patients (EF 2767%, N516). HF was de-fined by Framingham criteria using a standardized HF scoring system and the pres-ence of a BNPO400 pg/ml. We also examined whether corin levels were associated with other key parameters such as renal function and serum sodium that have path-ophysiologic significance in patients with HF. Results: LVSD with HF patients had much higher HF scores and BNP levels than controls or LVSD without HF patients. Corin levels were significantly lower in patients with LVSD with and without HF, than in controls (p!0.02). However, there was no significant difference between cor-in levels cor-in patients with LVSD without HF and those with HF (p50.765). Thus de-creased corin levels appeared to reflect LVSD rather than the presence of HF. Univariate analysis showed that higher serum [Na] was associated with higher corin levels (p50.001) consistent with a role in sodium balance. In multivariate analyses, despite adjustment for other factors, corin levels remained associated with serum so-dium levels (p5 0.003-0.04) and with systolic dysfunction (p5 0.007-0.065). Con-clusions: Corin levels are reduced in patients with reduced systolic function, independent of the presence of HF defined by Framingham criteria suggesting that the corin levels may serve as a biomarker or indicator of reduced contractility or vi-able myocardial mass. The link between corin and serum sodium levels suggests that corin activity may have a pathophysiologic role in regulating salt and water homeo-stasis in patients with cardiomyopathies.
033
Relationship between Inflammatory Biomarkers and Adiposity in Obese Patients with Heart Failure and Metabolic Syndrome
Marjan Motie, Vincent Kennedy, Lorraine S. Evangelista; University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA
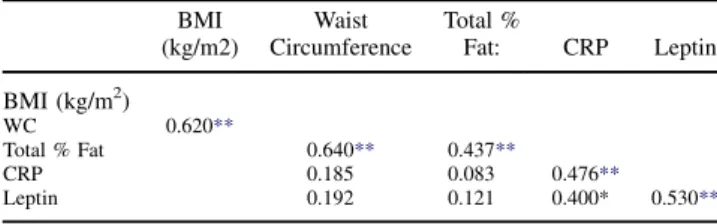
Background:Little is known about the associations between inflammation and obe-sity in patients with heart failure (HF) and metabolic syndrome (MS). The purpose of this report is to describe and evaluate the association between C-reactive protein (CRP), leptin, and adiposity in 36 obese patients with HF and MS. Method: Height and weight were used to calculate body mass index (BMI); adiposity was further as-sessed using waist circumference (WC) and body composition measures (e.g. percent body fat, percent lean mass) obtained from total body dual-energy x-ray absorptiom-etry (DEXA) scan. High sensitivity-CRP and leptin were measured using bioassays as standardized by our core lab. Results: Our data showed significant correlations be-tween CRP, leptin, and percent body fat (Table 1). In a post-hoc analyses, we com-pared leptin and CRP concentrations of patients with a BMIO35 (n 5 19) and patients with a BMI! 35 (n 5 13) and found that patients who were more obese had higher CRP (4,740m vs. 2,946m, p 5 0.019) and leptin (mean 48,953m vs. 26,795m, p5 0.009) levels than their counterpart. Conclusion: Our findings show that CRP and leptin were associated with adiposity in obese patients with HF and MS. Data from the sample also demonstrated that while the relationship between and CRP and leptin is independent of obesity level (i.e., were not significantly related to BMI or WC), there was a significant increase in the concentration of both of these markers in patients with a BMIO35. Future research that assess the potential impact of inflammation and adiposity and the role of dietary interventions and weight loss on clinical outcomes in this population of chronically ill patients are warranted.
Table 1.Correlation Matrix for Key Variables of Interest
BMI (kg/m2) Waist Circumference Total % Fat: CRP Leptin BMI (kg/m2) WC 0.620** Total % Fat 0.640** 0.437** CRP 0.185 0.083 0.476** Leptin 0.192 0.121 0.400* 0.530**
**Correlation is significant at the 0.01 level (2-tailed); * Correlation is significant at the 0.05 level (2-tailed).