84
Investigation of the effects of Coumaphos (ABvarC® ) and Flumethrin
(Varostop ®) on the control of Varroa destructor in honeybee (Apis
mellifera L.,) colonies and their effects on colony development,
U. Kumova, M. Çelik Güney, G.T. Kayaalp, M. Özdolap1Çukurova Universitesi, Faculty of Agriculture, Department of Animal Science, Adana-Turkey
Introduction
Varroa destructor (Anderson and Trueman, 2000) is a dangerous parasite that infects honey bees (Apis mellifera L.,) worldwide, causing significant economic losses in the beekeeping and agricultural area. Varroa is a very important problem that absorbs the blood of adult bees, larvae and pupae, weakens the colonies if left untreated, kills them and leads to the loss of bee products. In recent years, new form medicines with chemical and herbal active substances, which are practical and effective in practice, which do not require intensive labor force against Varroasis, have been introduced to the market. This study was carried out in the Çukurova region in the spring of 2016 in order to determine the efficacy of ABvarC® (Coumaphos) and Varostop® (Flumetrin) against Varroa destructor and the effects of colonies on population development.
Materials and methods
The study was carried out in 2016 (February 22-April 18) in 17 colonies selected randomly from colonies having the same strength colony population as queen bees reared from the same colonies (ItalianxCarniol hybrid). Colonies were randomly distributed in 3 different study groups (ABvarC, Varostop and Control). The experimental design used in the study consists of Group A (ABvarC), Group B (Varostop) and Group C (Control). ABvarC (Coumaphos) and Varostop (Flumethrin) were used as a chemical product for 5 weeks between February 29-April 4. Mavrik® (Fluvalinate) (April 4-April 11) was applied to the study group colonies (ABvarC, Varostop and Control) after trial. All the fallen varroa and dead bees were counted daily in colonies after chemical (5 weeks) and control application (1 week). The efficacy of the chemical and control applications was calculated with all the data obtained (Higes et al., 1997). The chemical and control applications on Varroa and bee in colony were tested in a completely randomized design. The mathematical model of completely randomized design is Yij = µ+ ∝�i�+ e�ij� i=1,2,...,t and j=1,2,...,r. Where µ is the mean effect, αi is the ith chemical and control applications effect, and eij is the term of error. The number of adult-brood bee population on frame (number / colony) and the adult-brood surface area (number/colony) of the colonies were estimated every 21 days by digital photograph machine in 3 measurement periods (29.02.2016-21.03.2016-11.04.2016) (Jeffree, 1951). It was determined whether chemical applications against Varroa had an effect on colony population development. The number of adult-brood bee population on frame and the adult-brood surface area of the colonies were tested in a randomized block design. The mathematical model of randomized block design is Yij = µ+ ∝�i�+ β�j�+ e�ij� i=1,2,...,t and j=1,2,...,b. Where µ is the mean effect, αi is the ith chemical and control applications effect, βj is the jth period effect, and eij is the term of error (Montgomery, 2001). Duncan test were used for multiple comparisons. Statistical analyses were calculated by using SPSS 22.0 V. package program.
85
Results
After chemical applications (35 days) and control application (7 days) in research colonies, the total number of dead varroa was determined. Efficacy of chemical and control applications on Varroa and bees in colony were determined and results are given with Table 1 and Table 2.
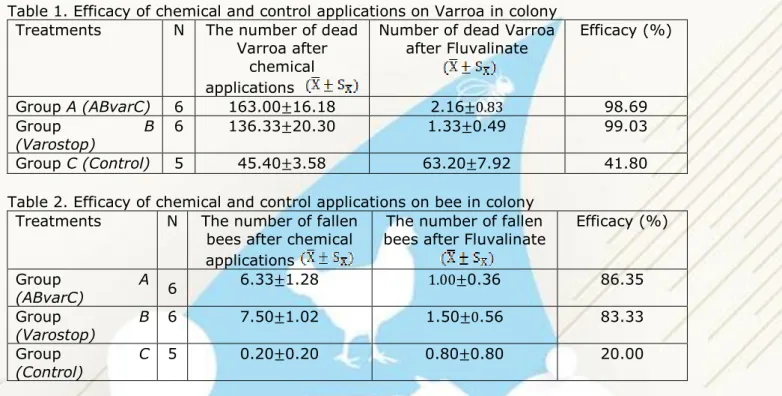
Table 1. Efficacy of chemical and control applications on Varroa in colony Treatments N The number of dead
Varroa after chemical applications
Number of dead Varroa
after Fluvalinate Efficacy (%)
Group A (ABvarC) 6 163.00±16.18 2.16±0.83 98.69
Group B
(Varostop)
6 136.33±20.30 1.33±0.49 99.03
Group C (Control) 5 45.40±3.58 63.20±7.92 41.80
Table 2. Efficacy of chemical and control applications on bee in colony Treatments N The number of fallen
bees after chemical applications
The number of fallen
bees after Fluvalinate Efficacy (%)
Group A (ABvarC) 6 6.33±1.28 1.00±0.36 86.35 Group B (Varostop) 6 7.50±1.02 1.50±0.56 83.33 Group C (Control) 5 0.20±0.20 0.80±0.80 20.00
When Table 1 has been examined, Varostop (Group B) (99.03%) has the highest effect on dead Varroa. Difference between groups is statistically significant (P<0.05). When Table 2 has been examined, ABvarC (Group A) (86.35%) has the highest effect on dead bees. Difference between groups is statistically not significant (P>0.05).
Effects of chemical applications on colony population development were examined and results are given with Table 3, Table 4, Table 5 and Table 6.
Table 3. The number of adult bee population on frames (number/colony) Treatments N Measurement Periods
29.02.2016c 21.03.2016b 11.04.2016a
Group A ab 6 4.00±0 5.83±0.47 7.16±0.47 5.66±0.31
Group B a 6 4.00±0 6.33±0.33 8.00±0.25 6.11±0.19
Group C b 5 4.00±0 4.80±0.48 6.20±0.66 5.00±0.38 4.00±0 5.65±0.42 7.12±0.46 5.59±0.29 When the difference between the periods have been examined, it is seen that the best period is April 11 with an average of 7.12 ± 0.46 (P <0.05). When the difference between the groups have been examined, it is seen that the best group is Group B (Varostop) with an average of 6.11 ± 0.19 (P <0.05).
86
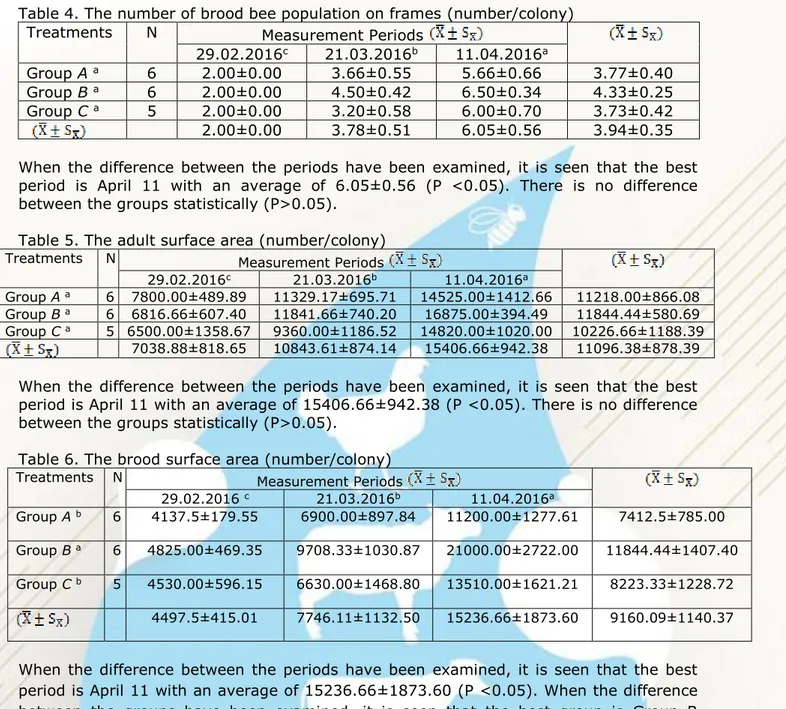
Table 4. The number of brood bee population on frames (number/colony) Treatments N Measurement Periods
29.02.2016c 21.03.2016b 11.04.2016a
Group A a 6 2.00±0.00 3.66±0.55 5.66±0.66 3.77±0.40 Group B a 6 2.00±0.00 4.50±0.42 6.50±0.34 4.33±0.25 Group C a 5 2.00±0.00 3.20±0.58 6.00±0.70 3.73±0.42 2.00±0.00 3.78±0.51 6.05±0.56 3.94±0.35 When the difference between the periods have been examined, it is seen that the best period is April 11 with an average of 6.05±0.56 (P <0.05). There is no difference between the groups statistically (P>0.05).
Table 5. The adult surface area (number/colony)
Treatments N Measurement Periods
29.02.2016c 21.03.2016b 11.04.2016a
Group A a 6 7800.00±489.89 11329.17±695.71 14525.00±1412.66 11218.00±866.08
Group B a 6 6816.66±607.40 11841.66±740.20 16875.00±394.49 11844.44±580.69
Group C a 5 6500.00±1358.67 9360.00±1186.52 14820.00±1020.00 10226.66±1188.39
7038.88±818.65 10843.61±874.14 15406.66±942.38 11096.38±878.39
When the difference between the periods have been examined, it is seen that the best period is April 11 with an average of 15406.66±942.38 (P <0.05). There is no difference between the groups statistically (P>0.05).
Table 6. The brood surface area (number/colony)
Treatments N Measurement Periods
29.02.2016 c 21.03.2016b 11.04.2016a
Group A b 6 4137.5±179.55 6900.00±897.84 11200.00±1277.61 7412.5±785.00
Group B a 6 4825.00±469.35 9708.33±1030.87 21000.00±2722.00 11844.44±1407.40
Group C b 5 4530.00±596.15 6630.00±1468.80 13510.00±1621.21 8223.33±1228.72
4497.5±415.01 7746.11±1132.50 15236.66±1873.60 9160.09±1140.37
When the difference between the periods have been examined, it is seen that the best period is April 11 with an average of 15236.66±1873.60 (P <0.05). When the difference between the groups have been examined, it is seen that the best group is Group B (Varostop) with an average of 11844.44±1407.40 (P <0.05).
Conclusion
As a result of the research, the efficacy of ABvarC® and Varostop® against V. destructor were found to be 98.69 % and 99.03 % respectively (Kumova, 2001; Gregorc and Smodiš Škerl, 2007; Smodiš Škerl et al., 2011; Mahmood et al., 2012; Girişgin et al., 2016). The efficacy of ABvarC® and Varostop® against bees were found to be 86.35% and 83.3 % respectively. The efficiency of ABvarC® and Varostop against Varroa destructor had been found significantly (P<0.05). No queens were lost in any of the colonies during the experiment. The ABvarC® and Varostop were also proved very effective for Varroa control. Honey bee parasitic Varroa destructor against of ABvarC® and Varostop can be used of more effective be advised to be applied to beekeepers.
87
References
Anderson, D.L. and Trueman, J.W.H. (2000). Varroa jacobsoni (Acari: Varroidae) is more than one species. Experimental & Applied Acarology, 24(3):165-189.
Girişgin, A., Özüiçli, O.M. and Aydın, L. (2016). Bal arılarında bazı kimyasal ilaçların varroosise karşı etkileri. 5 th International Muğla Beekeeping and Pine Honey Congress 1-5 November, 2016, Fethiye, Turkey.
Gregorc, A. and Smodiš Škerl, M.I. (2007). Combating Varroa destructor in honeybee colonies using Flumethrin or Fluvalinate. Acta Veterinaria Brno, 76(2):309-314. Higes, M., Liorente, J. and Suarez, M. (1997). Field trial on the effectiveness of Oxalic
acid in the control of Varroatosis in Apis mellifera colonies. XXXVth International Apicultural Congress of Apimondia. 1-6 September. Antrep-Belgium. 227/445. Jeffree, E.P. (1951). A photographic presentation of estimated numbers of Honeybees
(Apis mellifera) on combs in 14 ×8 inch frames. Bee World, 32: 89–91.
Kumova, U. (2001). The Investigation on the effects of some chemicals used to control Varroa jacobsoni in Turkey. Turkish J. of Vet.&Anim. Sci., 25:597-602.
Mahmood, R., Stephen Wagchoure, E., Raja, S. and Sarwar, G. (2012). Control of Varroa destructor using Oxalic acid, Formic acid and Bayvarol Strip in Apis mellifera (Hymenoptera: Apidae) Colonies. Pakistan J. Zool., 44(6):1473-1477.
Montgomery, D.C. (2001). Design and analysis and experiments. John Wiley-Sons, New York.
Smodiš Škerl, M.I., Nakrst, M., Žvokelj, L. and Gregorc, A. (2011). The acaricidal effect of Flumethrin, Oxalic acid and Amitraz against Varroa destructor in honey bee (Apis mellifera carnica) colonies. Acta Veterinaria Brno, 80(1):51-56.